# `AMR`
### An [R package](https://www.r-project.org) to simplify the analysis and prediction of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and work with antibiotic properties by using evidence-based methods.
This R package was created for academic research by PhD students of the Faculty of Medical Sciences of the [University of Groningen](https://www.rug.nl) and the Medical Microbiology & Infection Prevention (MMBI) department of the [University Medical Center Groningen (UMCG)](https://www.umcg.nl).
:arrow_forward: Get it with `install.packages("AMR")` or see below for other possibilities. Read all changes and new functions in [NEWS.md](NEWS.md).
## Authors
 Matthijs S. Berends1,2,a,
Matthijs S. Berends1,2,a,
 Christian F. Luz1,a,
Erwin E.A. Hassing2,
Christian F. Luz1,a,
Erwin E.A. Hassing2,
 Corinna Glasner1,b,
Corinna Glasner1,b,
 Alex W. Friedrich1,b,
Alex W. Friedrich1,b,
 Bhanu Sinha1,b
1 Department of Medical Microbiology, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, the Netherlands - [rug.nl](http://www.rug.nl) [umcg.nl](http://www.umcg.nl)
Bhanu Sinha1,b
1 Department of Medical Microbiology, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, the Netherlands - [rug.nl](http://www.rug.nl) [umcg.nl](http://www.umcg.nl)
2 Certe Medical Diagnostics & Advice, Groningen, the Netherlands - [certe.nl](http://www.certe.nl)
a R package author and thesis dissertant
b Thesis advisor




 ## Contents
* [Why this package?](#why-this-package)
* [How to get it?](#how-to-get-it)
* [Install from CRAN](#install-from-cran)
* [Install from GitHub](#install-from-github)
* [How to use it?](#how-to-use-it)
* [New classes](#new-classes)
* [Overwrite/force resistance based on EUCAST rules](#overwriteforce-resistance-based-on-eucast-rules)
* [Other (microbial) epidemiological functions](#other-microbial-epidemiological-functions)
* [Frequency tables](#frequency-tables)
* [Data sets included in package](#data-sets-included-in-package)
* [Copyright](#copyright)
## Why this package?
This R package was intended to make microbial epidemiology easier. Most functions contain extensive help pages to get started.
This `AMR` package basically does four important things:
1. It **cleanses existing data**, by transforming it to reproducible and profound *classes*, making the most efficient use of R. These function all use artificial intelligence to get expected results:
* Use `as.bactid` to get an ID of a microorganism. It takes almost any text as input that looks like the name or code of a microorganism like "E. coli", "esco" and "esccol". Moreover, it can group all coagulase negative and positive *Staphylococci*, and can transform *Streptococci* into Lancefield groups. This package has a database of ~2500 different (potential) human pathogenic microorganisms.
* Use `as.rsi` to transform values to valid antimicrobial results. It produces just S, I or R based on your input and warns about invalid values. Even values like "<=0.002; S" (combined MIC/RSI) will result in "S".
* Use `as.mic` to cleanse your MIC values. It produces a so-called factor (in SPSS calls this *ordinal*) with valid MIC values as levels. A value like "<=0.002; S" (combined MIC/RSI) will result in "<=0.002".
* Use `as.atc` to get the ATC code of an antibiotic as defined by the WHO. This package contains a database with most LIS codes, official names, DDDs and even trade names of antibiotics. For example, the values "Furabid", "Furadantine", "nitro" will return the ATC code of Nitrofurantoine.
2. It **enhances existing data** and **adds new data** from data sets included in this package.
* Use `EUCAST_rules` to apply [EUCAST expert rules to isolates](http://www.eucast.org/expert_rules_and_intrinsic_resistance/).
* Use `MDRO` (abbreviation of Multi Drug Resistant Organisms) to check your isolates for exceptional resistance with country-specific guidelines with or EUCAST rules. Currently, national guidelines for Germany and the Netherlands are supported.
* Data set `microorganisms` contains the family, genus, species, subspecies, colloqual name and Gram stain of almost 2500 microorganisms. This enables e.g. resistance analysis of different antibiotics per Gram stain.
* Data set `antibiotics` contains the ATC code, LIS codes, official name, trivial name, trade name and DDD of both oral and parenteral administration.
* Use `first_isolate` to identify the first isolates of every patient [using guidelines from the CLSI](https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m39/) (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute). * You can also identify first *weighted* isolates of every patient, an adjusted version of the CLSI guideline. This takes into account key antibiotics of every strain and compares them.
3. It **analyses the data** with convenient functions that use well-known methods.
* Calculate the resistance (and even co-resistance) of microbial isolates with the `portion_R`, `portion_IR`, `portion_I`, `portion_SI` and `portion_S` functions, that can also be used with the `dplyr` package (e.g. in conjunction with `summarise`)
* Plot AMR results with `geom_rsi`, a function made for the `ggplot2` package
* Predict antimicrobial resistance for the nextcoming years using logistic regression models with the `resistance_predict` function
* Conduct descriptive statistics to enhance base R: calculate kurtosis, skewness and create frequency tables
4. It **teaches the user** how to use all the above actions, by showing many examples in the help pages. The package contains an example data set called `septic_patients`. This data set, consisting of 2000 blood culture isolates from anonymised septic patients between 2001 and 2017 in the Northern Netherlands, is real and genuine data.
## How to get it?
All versions of this package [are published on CRAN](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR), the official R network with a peer-reviewed submission process.
### Install from CRAN
[](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR) [](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR)
(Note: Downloads measured only by [cran.rstudio.com](https://cran.rstudio.com/package=AMR), this excludes e.g. the official [cran.r-project.org](https://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR))
-
## Contents
* [Why this package?](#why-this-package)
* [How to get it?](#how-to-get-it)
* [Install from CRAN](#install-from-cran)
* [Install from GitHub](#install-from-github)
* [How to use it?](#how-to-use-it)
* [New classes](#new-classes)
* [Overwrite/force resistance based on EUCAST rules](#overwriteforce-resistance-based-on-eucast-rules)
* [Other (microbial) epidemiological functions](#other-microbial-epidemiological-functions)
* [Frequency tables](#frequency-tables)
* [Data sets included in package](#data-sets-included-in-package)
* [Copyright](#copyright)
## Why this package?
This R package was intended to make microbial epidemiology easier. Most functions contain extensive help pages to get started.
This `AMR` package basically does four important things:
1. It **cleanses existing data**, by transforming it to reproducible and profound *classes*, making the most efficient use of R. These function all use artificial intelligence to get expected results:
* Use `as.bactid` to get an ID of a microorganism. It takes almost any text as input that looks like the name or code of a microorganism like "E. coli", "esco" and "esccol". Moreover, it can group all coagulase negative and positive *Staphylococci*, and can transform *Streptococci* into Lancefield groups. This package has a database of ~2500 different (potential) human pathogenic microorganisms.
* Use `as.rsi` to transform values to valid antimicrobial results. It produces just S, I or R based on your input and warns about invalid values. Even values like "<=0.002; S" (combined MIC/RSI) will result in "S".
* Use `as.mic` to cleanse your MIC values. It produces a so-called factor (in SPSS calls this *ordinal*) with valid MIC values as levels. A value like "<=0.002; S" (combined MIC/RSI) will result in "<=0.002".
* Use `as.atc` to get the ATC code of an antibiotic as defined by the WHO. This package contains a database with most LIS codes, official names, DDDs and even trade names of antibiotics. For example, the values "Furabid", "Furadantine", "nitro" will return the ATC code of Nitrofurantoine.
2. It **enhances existing data** and **adds new data** from data sets included in this package.
* Use `EUCAST_rules` to apply [EUCAST expert rules to isolates](http://www.eucast.org/expert_rules_and_intrinsic_resistance/).
* Use `MDRO` (abbreviation of Multi Drug Resistant Organisms) to check your isolates for exceptional resistance with country-specific guidelines with or EUCAST rules. Currently, national guidelines for Germany and the Netherlands are supported.
* Data set `microorganisms` contains the family, genus, species, subspecies, colloqual name and Gram stain of almost 2500 microorganisms. This enables e.g. resistance analysis of different antibiotics per Gram stain.
* Data set `antibiotics` contains the ATC code, LIS codes, official name, trivial name, trade name and DDD of both oral and parenteral administration.
* Use `first_isolate` to identify the first isolates of every patient [using guidelines from the CLSI](https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m39/) (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute). * You can also identify first *weighted* isolates of every patient, an adjusted version of the CLSI guideline. This takes into account key antibiotics of every strain and compares them.
3. It **analyses the data** with convenient functions that use well-known methods.
* Calculate the resistance (and even co-resistance) of microbial isolates with the `portion_R`, `portion_IR`, `portion_I`, `portion_SI` and `portion_S` functions, that can also be used with the `dplyr` package (e.g. in conjunction with `summarise`)
* Plot AMR results with `geom_rsi`, a function made for the `ggplot2` package
* Predict antimicrobial resistance for the nextcoming years using logistic regression models with the `resistance_predict` function
* Conduct descriptive statistics to enhance base R: calculate kurtosis, skewness and create frequency tables
4. It **teaches the user** how to use all the above actions, by showing many examples in the help pages. The package contains an example data set called `septic_patients`. This data set, consisting of 2000 blood culture isolates from anonymised septic patients between 2001 and 2017 in the Northern Netherlands, is real and genuine data.
## How to get it?
All versions of this package [are published on CRAN](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR), the official R network with a peer-reviewed submission process.
### Install from CRAN
[](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR) [](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR)
(Note: Downloads measured only by [cran.rstudio.com](https://cran.rstudio.com/package=AMR), this excludes e.g. the official [cran.r-project.org](https://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR))
-  Install using [RStudio](http://www.rstudio.com) (recommended):
- Click on `Tools` and then `Install Packages...`
- Type in `AMR` and press Install
-
Install using [RStudio](http://www.rstudio.com) (recommended):
- Click on `Tools` and then `Install Packages...`
- Type in `AMR` and press Install
-  Install in R directly:
- `install.packages("AMR")`
### Install from GitHub
This is the latest development version. Although it may contain bugfixes and even new functions compared to the latest released version on CRAN, it is also subject to change and may be unstable or behave unexpectedly. Always consider this a beta version.
[](https://travis-ci.org/msberends/AMR)
[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/msberends/AMR)
[](https://github.com/msberends/AMR/commits/master)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/msberends/AMR)
```r
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("msberends/AMR")
```
### Install from Zenodo
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1305355)
This package was also published on Zenodo: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1305355
## How to use it?
```r
# Call it with:
library(AMR)
# For a list of functions:
help(package = "AMR")
```
### New classes
This package contains two new S3 classes: `mic` for MIC values (e.g. from Vitek or Phoenix) and `rsi` for antimicrobial drug interpretations (i.e. S, I and R). Both are actually ordered factors under the hood (an MIC of `2` being higher than `<=1` but lower than `>=32`, and for class `rsi` factors are ordered as `S < I < R`).
Both classes have extensions for existing generic functions like `print`, `summary` and `plot`.
These functions also try to coerce valid values.
#### RSI
The `septic_patients` data set comes with antimicrobial results of more than 40 different drugs. For example, columns `amox` and `cipr` contain results of amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin, respectively.
```r
summary(septic_patients[, c("amox", "cipr")])
# amox cipr
# Mode :rsi Mode :rsi
# :1002 :596
# Sum S :336 Sum S :1108
# Sum IR:662 Sum IR:296
# -Sum R:659 -Sum R:227
# -Sum I:3 -Sum I:69
```
You can use the `plot` function from base R:
```r
plot(septic_patients$cipr)
```
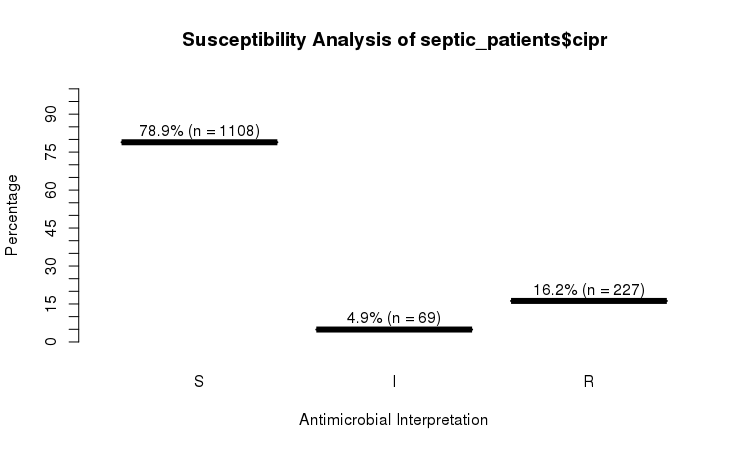
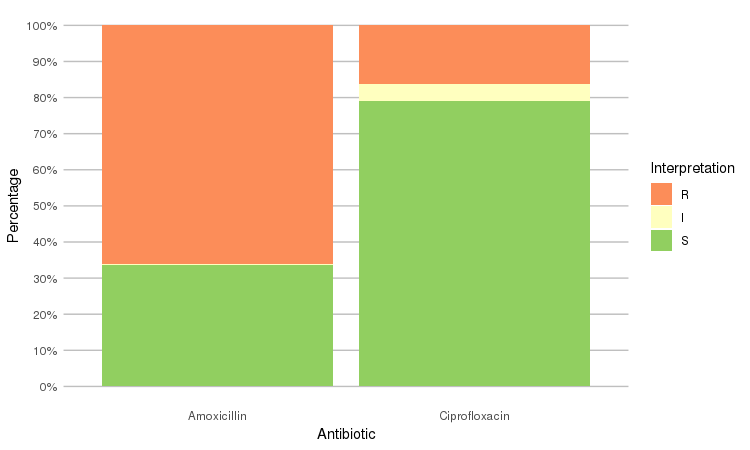
Or use the `ggplot2` and `dplyr` packages to create more appealing plots:
```r
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
septic_patients %>%
select(amox, cipr) %>%
ggplot_rsi()
```
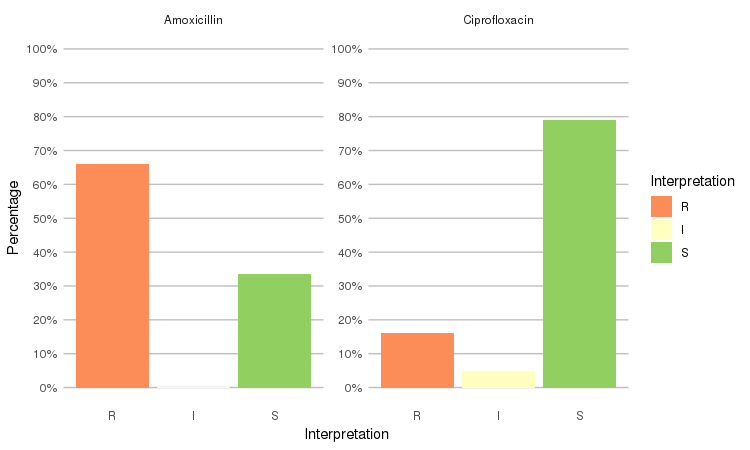
```r
septic_patients %>%
select(amox, cipr) %>%
ggplot_rsi(x = "Interpretation", facet = "Antibiotic")
```
It also supports grouping variables. Let's say we want to compare resistance of drugs against Urine Tract Infections (UTI) between hospitals A to D (variable `hospital_id`):
```r
septic_patients %>%
select(hospital_id, amox, nitr, fosf, trim, cipr) %>%
group_by(hospital_id) %>%
ggplot_rsi(x = "hospital_id",
facet = "Antibiotic",
nrow = 1) +
labs(title = "AMR of Anti-UTI Drugs Per Hospital",
x = "Hospital")
```
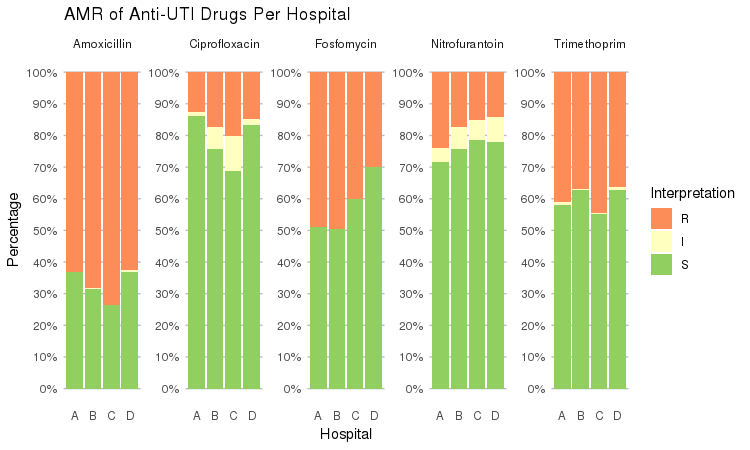
You could use this to group on anything in your plots: Gram stain, age (group), genus, geographic location, et cetera.
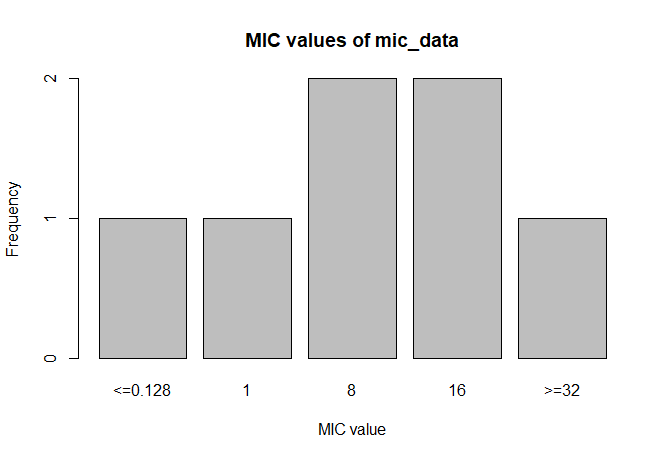
#### MIC
```r
# Transform values to new class
mic_data <- as.mic(c(">=32", "1.0", "8", "<=0.128", "8", "16", "16"))
summary(mic_data)
# Mode:mic
# :0
# Min.:<=0.128
# Max.:>=32
plot(mic_data)
```
### Overwrite/force resistance based on EUCAST rules
This is also called *interpretive reading*.
```r
before <- data.frame(bactid = c("STAAUR", # Staphylococcus aureus
"ENCFAE", # Enterococcus faecalis
"ESCCOL", # Escherichia coli
"KLEPNE", # Klebsiella pneumoniae
"PSEAER"), # Pseudomonas aeruginosa
vanc = "-", # Vancomycin
amox = "-", # Amoxicillin
coli = "-", # Colistin
cfta = "-", # Ceftazidime
cfur = "-", # Cefuroxime
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
before
# bactid vanc amox coli cfta cfur
# 1 STAAUR - - - - -
# 2 ENCFAE - - - - -
# 3 ESCCOL - - - - -
# 4 KLEPNE - - - - -
# 5 PSEAER - - - - -
# Now apply those rules; just need a column with bacteria ID's and antibiotic results:
after <- EUCAST_rules(before)
after
# bactid vanc amox coli cfta cfur
# 1 STAAUR - - R R -
# 2 ENCFAE - - R R R
# 3 ESCCOL R - - - -
# 4 KLEPNE R R - - -
# 5 PSEAER R R - - R
```
Bacteria ID's can be retrieved with the `guess_bactid` function. It uses any type of info about a microorganism as input. For example, all these will return value `STAAUR`, the ID of *S. aureus*:
```r
guess_bactid("stau")
guess_bactid("STAU")
guess_bactid("staaur")
guess_bactid("S. aureus")
guess_bactid("S aureus")
guess_bactid("Staphylococcus aureus")
guess_bactid("MRSA") # Methicillin Resistant S. aureus
guess_bactid("VISA") # Vancomycin Intermediate S. aureus
guess_bactid("VRSA") # Vancomycin Resistant S. aureus
```
### Other (microbial) epidemiological functions
```r
# G-test to replace Chi squared test
g.test(...)
# Determine key antibiotic based on bacteria ID
key_antibiotics(...)
# Selection of first isolates of any patient
first_isolate(...)
# Calculate resistance levels of antibiotics, can be used with `summarise` (dplyr)
rsi(...)
# Predict resistance levels of antibiotics
rsi_predict(...)
# Get name of antibiotic by ATC code
abname(...)
abname("J01CR02", from = "atc", to = "umcg") # "AMCL"
```
### Frequency tables
Base R lacks a simple function to create frequency tables. We created such a function that works with almost all data types: `freq` (or `frequency_tbl`). It can be used in two ways:
```r
# Like base R:
freq(mydata$myvariable)
# And like tidyverse:
mydata %>% freq(myvariable)
```
Factors sort on item by default:
```r
septic_patients %>% freq(hospital_id)
# Frequency table of `hospital_id`
# Class: factor
# Length: 2000 (of which NA: 0 = 0.0%)
# Unique: 4
#
# Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent (Factor Level)
# --- ----- ------ -------- ----------- ------------- ---------------
# 1 A 319 16.0% 319 16.0% 1
# 2 B 661 33.1% 980 49.0% 2
# 3 C 256 12.8% 1236 61.8% 3
# 4 D 764 38.2% 2000 100.0% 4
```
This can be changed with the `sort.count` parameter:
```r
septic_patients %>% freq(hospital_id, sort.count = TRUE)
# Frequency table of `hospital_id`
# Class: factor
# Length: 2000 (of which NA: 0 = 0.0%)
# Unique: 4
#
# Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent (Factor Level)
# --- ----- ------ -------- ----------- ------------- ---------------
# 1 D 764 38.2% 764 38.2% 4
# 2 B 661 33.1% 1425 71.2% 2
# 3 A 319 16.0% 1744 87.2% 1
# 4 C 256 12.8% 2000 100.0% 3
```
All other types, like numbers, characters and dates, sort on count by default:
```r
septic_patients %>% freq(date)
# Frequency table of `date`
# Class: Date
# Length: 2000 (of which NA: 0 = 0.0%)
# Unique: 1151
#
# Oldest: 2 January 2002
# Newest: 28 December 2017 (+5839)
# Median: 7 Augustus 2009 (~48%)
#
# Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent
# --- ----------- ------ -------- ----------- -------------
# 1 2016-05-21 10 0.5% 10 0.5%
# 2 2004-11-15 8 0.4% 18 0.9%
# 3 2013-07-29 8 0.4% 26 1.3%
# 4 2017-06-12 8 0.4% 34 1.7%
# 5 2015-11-19 7 0.4% 41 2.1%
# 6 2005-12-22 6 0.3% 47 2.4%
# 7 2015-10-12 6 0.3% 53 2.6%
# 8 2002-05-16 5 0.2% 58 2.9%
# 9 2004-02-02 5 0.2% 63 3.1%
# 10 2004-02-18 5 0.2% 68 3.4%
# 11 2005-08-16 5 0.2% 73 3.6%
# 12 2005-09-01 5 0.2% 78 3.9%
# 13 2006-06-29 5 0.2% 83 4.2%
# 14 2007-08-10 5 0.2% 88 4.4%
# 15 2008-08-29 5 0.2% 93 4.7%
# [ reached getOption("max.print.freq") -- omitted 1136 entries, n = 1907 (95.3%) ]
```
For numeric values, some extra descriptive statistics will be calculated:
```r
freq(runif(n = 10, min = 1, max = 5))
# Frequency table
# Class: numeric
# Length: 10 (of which NA: 0 = 0.0%)
# Unique: 10
#
# Mean: 3.4
# Std. dev.: 1.3 (CV: 0.38, MAD: 1.3)
# Five-Num: 1.6 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 4.7 | 4.8 (IQR: 2.7, CQV: 0.4)
# Outliers: 0
#
# Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent
# --- --------- ------ -------- ----------- -------------
# 1 1.568997 1 10.0% 1 10.0%
# 2 1.993575 1 10.0% 2 20.0%
# 3 2.022348 1 10.0% 3 30.0%
# 4 2.236038 1 10.0% 4 40.0%
# 5 3.579828 1 10.0% 5 50.0%
# 6 4.178081 1 10.0% 6 60.0%
# 7 4.394818 1 10.0% 7 70.0%
# 8 4.689871 1 10.0% 8 80.0%
# 9 4.698626 1 10.0% 9 90.0%
# 10 4.751488 1 10.0% 10 100.0%
#
# Warning message:
# All observations are unique.
```
Learn more about this function with:
```r
?freq
```
### Data sets included in package
Datasets to work with antibiotics and bacteria properties.
```r
# Dataset with 2000 random blood culture isolates from anonymised
# septic patients between 2001 and 2017 in 5 Dutch hospitals
septic_patients # A tibble: 2,000 x 49
# Dataset with ATC antibiotics codes, official names, trade names
# and DDD's (oral and parenteral)
antibiotics # A tibble: 420 x 18
# Dataset with bacteria codes and properties like gram stain and
# aerobic/anaerobic
microorganisms # A tibble: 2,453 x 12
```
## Copyright
[](https://github.com/msberends/AMR/blob/master/LICENSE)
This R package is licensed under the [GNU General Public License (GPL) v2.0](https://github.com/msberends/AMR/blob/master/LICENSE). In a nutshell, this means that this package:
- May be used for commercial purposes
- May be used for private purposes
- May **not** be used for patent purposes
- May be modified, although:
- Modifications **must** be released under the same license when distributing the package
- Changes made to the code **must** be documented
- May be distributed, although:
- Source code **must** be made available when the package is distributed
- A copy of the license and copyright notice **must** be included with the package.
- Comes with a LIMITATION of liability
- Comes with NO warranty
Install in R directly:
- `install.packages("AMR")`
### Install from GitHub
This is the latest development version. Although it may contain bugfixes and even new functions compared to the latest released version on CRAN, it is also subject to change and may be unstable or behave unexpectedly. Always consider this a beta version.
[](https://travis-ci.org/msberends/AMR)
[](https://ci.appveyor.com/project/msberends/AMR)
[](https://github.com/msberends/AMR/commits/master)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/msberends/AMR)
```r
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("msberends/AMR")
```
### Install from Zenodo
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1305355)
This package was also published on Zenodo: https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1305355
## How to use it?
```r
# Call it with:
library(AMR)
# For a list of functions:
help(package = "AMR")
```
### New classes
This package contains two new S3 classes: `mic` for MIC values (e.g. from Vitek or Phoenix) and `rsi` for antimicrobial drug interpretations (i.e. S, I and R). Both are actually ordered factors under the hood (an MIC of `2` being higher than `<=1` but lower than `>=32`, and for class `rsi` factors are ordered as `S < I < R`).
Both classes have extensions for existing generic functions like `print`, `summary` and `plot`.
These functions also try to coerce valid values.
#### RSI
The `septic_patients` data set comes with antimicrobial results of more than 40 different drugs. For example, columns `amox` and `cipr` contain results of amoxicillin and ciprofloxacin, respectively.
```r
summary(septic_patients[, c("amox", "cipr")])
# amox cipr
# Mode :rsi Mode :rsi
# :1002 :596
# Sum S :336 Sum S :1108
# Sum IR:662 Sum IR:296
# -Sum R:659 -Sum R:227
# -Sum I:3 -Sum I:69
```
You can use the `plot` function from base R:
```r
plot(septic_patients$cipr)
```

Or use the `ggplot2` and `dplyr` packages to create more appealing plots:
```r
library(dplyr)
library(ggplot2)
septic_patients %>%
select(amox, cipr) %>%
ggplot_rsi()
```

```r
septic_patients %>%
select(amox, cipr) %>%
ggplot_rsi(x = "Interpretation", facet = "Antibiotic")
```

It also supports grouping variables. Let's say we want to compare resistance of drugs against Urine Tract Infections (UTI) between hospitals A to D (variable `hospital_id`):
```r
septic_patients %>%
select(hospital_id, amox, nitr, fosf, trim, cipr) %>%
group_by(hospital_id) %>%
ggplot_rsi(x = "hospital_id",
facet = "Antibiotic",
nrow = 1) +
labs(title = "AMR of Anti-UTI Drugs Per Hospital",
x = "Hospital")
```

You could use this to group on anything in your plots: Gram stain, age (group), genus, geographic location, et cetera.
#### MIC
```r
# Transform values to new class
mic_data <- as.mic(c(">=32", "1.0", "8", "<=0.128", "8", "16", "16"))
summary(mic_data)
# Mode:mic
# :0
# Min.:<=0.128
# Max.:>=32
plot(mic_data)
```

### Overwrite/force resistance based on EUCAST rules
This is also called *interpretive reading*.
```r
before <- data.frame(bactid = c("STAAUR", # Staphylococcus aureus
"ENCFAE", # Enterococcus faecalis
"ESCCOL", # Escherichia coli
"KLEPNE", # Klebsiella pneumoniae
"PSEAER"), # Pseudomonas aeruginosa
vanc = "-", # Vancomycin
amox = "-", # Amoxicillin
coli = "-", # Colistin
cfta = "-", # Ceftazidime
cfur = "-", # Cefuroxime
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
before
# bactid vanc amox coli cfta cfur
# 1 STAAUR - - - - -
# 2 ENCFAE - - - - -
# 3 ESCCOL - - - - -
# 4 KLEPNE - - - - -
# 5 PSEAER - - - - -
# Now apply those rules; just need a column with bacteria ID's and antibiotic results:
after <- EUCAST_rules(before)
after
# bactid vanc amox coli cfta cfur
# 1 STAAUR - - R R -
# 2 ENCFAE - - R R R
# 3 ESCCOL R - - - -
# 4 KLEPNE R R - - -
# 5 PSEAER R R - - R
```
Bacteria ID's can be retrieved with the `guess_bactid` function. It uses any type of info about a microorganism as input. For example, all these will return value `STAAUR`, the ID of *S. aureus*:
```r
guess_bactid("stau")
guess_bactid("STAU")
guess_bactid("staaur")
guess_bactid("S. aureus")
guess_bactid("S aureus")
guess_bactid("Staphylococcus aureus")
guess_bactid("MRSA") # Methicillin Resistant S. aureus
guess_bactid("VISA") # Vancomycin Intermediate S. aureus
guess_bactid("VRSA") # Vancomycin Resistant S. aureus
```
### Other (microbial) epidemiological functions
```r
# G-test to replace Chi squared test
g.test(...)
# Determine key antibiotic based on bacteria ID
key_antibiotics(...)
# Selection of first isolates of any patient
first_isolate(...)
# Calculate resistance levels of antibiotics, can be used with `summarise` (dplyr)
rsi(...)
# Predict resistance levels of antibiotics
rsi_predict(...)
# Get name of antibiotic by ATC code
abname(...)
abname("J01CR02", from = "atc", to = "umcg") # "AMCL"
```
### Frequency tables
Base R lacks a simple function to create frequency tables. We created such a function that works with almost all data types: `freq` (or `frequency_tbl`). It can be used in two ways:
```r
# Like base R:
freq(mydata$myvariable)
# And like tidyverse:
mydata %>% freq(myvariable)
```
Factors sort on item by default:
```r
septic_patients %>% freq(hospital_id)
# Frequency table of `hospital_id`
# Class: factor
# Length: 2000 (of which NA: 0 = 0.0%)
# Unique: 4
#
# Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent (Factor Level)
# --- ----- ------ -------- ----------- ------------- ---------------
# 1 A 319 16.0% 319 16.0% 1
# 2 B 661 33.1% 980 49.0% 2
# 3 C 256 12.8% 1236 61.8% 3
# 4 D 764 38.2% 2000 100.0% 4
```
This can be changed with the `sort.count` parameter:
```r
septic_patients %>% freq(hospital_id, sort.count = TRUE)
# Frequency table of `hospital_id`
# Class: factor
# Length: 2000 (of which NA: 0 = 0.0%)
# Unique: 4
#
# Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent (Factor Level)
# --- ----- ------ -------- ----------- ------------- ---------------
# 1 D 764 38.2% 764 38.2% 4
# 2 B 661 33.1% 1425 71.2% 2
# 3 A 319 16.0% 1744 87.2% 1
# 4 C 256 12.8% 2000 100.0% 3
```
All other types, like numbers, characters and dates, sort on count by default:
```r
septic_patients %>% freq(date)
# Frequency table of `date`
# Class: Date
# Length: 2000 (of which NA: 0 = 0.0%)
# Unique: 1151
#
# Oldest: 2 January 2002
# Newest: 28 December 2017 (+5839)
# Median: 7 Augustus 2009 (~48%)
#
# Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent
# --- ----------- ------ -------- ----------- -------------
# 1 2016-05-21 10 0.5% 10 0.5%
# 2 2004-11-15 8 0.4% 18 0.9%
# 3 2013-07-29 8 0.4% 26 1.3%
# 4 2017-06-12 8 0.4% 34 1.7%
# 5 2015-11-19 7 0.4% 41 2.1%
# 6 2005-12-22 6 0.3% 47 2.4%
# 7 2015-10-12 6 0.3% 53 2.6%
# 8 2002-05-16 5 0.2% 58 2.9%
# 9 2004-02-02 5 0.2% 63 3.1%
# 10 2004-02-18 5 0.2% 68 3.4%
# 11 2005-08-16 5 0.2% 73 3.6%
# 12 2005-09-01 5 0.2% 78 3.9%
# 13 2006-06-29 5 0.2% 83 4.2%
# 14 2007-08-10 5 0.2% 88 4.4%
# 15 2008-08-29 5 0.2% 93 4.7%
# [ reached getOption("max.print.freq") -- omitted 1136 entries, n = 1907 (95.3%) ]
```
For numeric values, some extra descriptive statistics will be calculated:
```r
freq(runif(n = 10, min = 1, max = 5))
# Frequency table
# Class: numeric
# Length: 10 (of which NA: 0 = 0.0%)
# Unique: 10
#
# Mean: 3.4
# Std. dev.: 1.3 (CV: 0.38, MAD: 1.3)
# Five-Num: 1.6 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 4.7 | 4.8 (IQR: 2.7, CQV: 0.4)
# Outliers: 0
#
# Item Count Percent Cum. Count Cum. Percent
# --- --------- ------ -------- ----------- -------------
# 1 1.568997 1 10.0% 1 10.0%
# 2 1.993575 1 10.0% 2 20.0%
# 3 2.022348 1 10.0% 3 30.0%
# 4 2.236038 1 10.0% 4 40.0%
# 5 3.579828 1 10.0% 5 50.0%
# 6 4.178081 1 10.0% 6 60.0%
# 7 4.394818 1 10.0% 7 70.0%
# 8 4.689871 1 10.0% 8 80.0%
# 9 4.698626 1 10.0% 9 90.0%
# 10 4.751488 1 10.0% 10 100.0%
#
# Warning message:
# All observations are unique.
```
Learn more about this function with:
```r
?freq
```
### Data sets included in package
Datasets to work with antibiotics and bacteria properties.
```r
# Dataset with 2000 random blood culture isolates from anonymised
# septic patients between 2001 and 2017 in 5 Dutch hospitals
septic_patients # A tibble: 2,000 x 49
# Dataset with ATC antibiotics codes, official names, trade names
# and DDD's (oral and parenteral)
antibiotics # A tibble: 420 x 18
# Dataset with bacteria codes and properties like gram stain and
# aerobic/anaerobic
microorganisms # A tibble: 2,453 x 12
```
## Copyright
[](https://github.com/msberends/AMR/blob/master/LICENSE)
This R package is licensed under the [GNU General Public License (GPL) v2.0](https://github.com/msberends/AMR/blob/master/LICENSE). In a nutshell, this means that this package:
- May be used for commercial purposes
- May be used for private purposes
- May **not** be used for patent purposes
- May be modified, although:
- Modifications **must** be released under the same license when distributing the package
- Changes made to the code **must** be documented
- May be distributed, although:
- Source code **must** be made available when the package is distributed
- A copy of the license and copyright notice **must** be included with the package.
- Comes with a LIMITATION of liability
- Comes with NO warranty




 ## Contents
* [Why this package?](#why-this-package)
* [How to get it?](#how-to-get-it)
* [Install from CRAN](#install-from-cran)
* [Install from GitHub](#install-from-github)
* [How to use it?](#how-to-use-it)
* [New classes](#new-classes)
* [Overwrite/force resistance based on EUCAST rules](#overwriteforce-resistance-based-on-eucast-rules)
* [Other (microbial) epidemiological functions](#other-microbial-epidemiological-functions)
* [Frequency tables](#frequency-tables)
* [Data sets included in package](#data-sets-included-in-package)
* [Copyright](#copyright)
## Why this package?
This R package was intended to make microbial epidemiology easier. Most functions contain extensive help pages to get started.
This `AMR` package basically does four important things:
1. It **cleanses existing data**, by transforming it to reproducible and profound *classes*, making the most efficient use of R. These function all use artificial intelligence to get expected results:
* Use `as.bactid` to get an ID of a microorganism. It takes almost any text as input that looks like the name or code of a microorganism like "E. coli", "esco" and "esccol". Moreover, it can group all coagulase negative and positive *Staphylococci*, and can transform *Streptococci* into Lancefield groups. This package has a database of ~2500 different (potential) human pathogenic microorganisms.
* Use `as.rsi` to transform values to valid antimicrobial results. It produces just S, I or R based on your input and warns about invalid values. Even values like "<=0.002; S" (combined MIC/RSI) will result in "S".
* Use `as.mic` to cleanse your MIC values. It produces a so-called factor (in SPSS calls this *ordinal*) with valid MIC values as levels. A value like "<=0.002; S" (combined MIC/RSI) will result in "<=0.002".
* Use `as.atc` to get the ATC code of an antibiotic as defined by the WHO. This package contains a database with most LIS codes, official names, DDDs and even trade names of antibiotics. For example, the values "Furabid", "Furadantine", "nitro" will return the ATC code of Nitrofurantoine.
2. It **enhances existing data** and **adds new data** from data sets included in this package.
* Use `EUCAST_rules` to apply [EUCAST expert rules to isolates](http://www.eucast.org/expert_rules_and_intrinsic_resistance/).
* Use `MDRO` (abbreviation of Multi Drug Resistant Organisms) to check your isolates for exceptional resistance with country-specific guidelines with or EUCAST rules. Currently, national guidelines for Germany and the Netherlands are supported.
* Data set `microorganisms` contains the family, genus, species, subspecies, colloqual name and Gram stain of almost 2500 microorganisms. This enables e.g. resistance analysis of different antibiotics per Gram stain.
* Data set `antibiotics` contains the ATC code, LIS codes, official name, trivial name, trade name and DDD of both oral and parenteral administration.
* Use `first_isolate` to identify the first isolates of every patient [using guidelines from the CLSI](https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m39/) (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute). * You can also identify first *weighted* isolates of every patient, an adjusted version of the CLSI guideline. This takes into account key antibiotics of every strain and compares them.
3. It **analyses the data** with convenient functions that use well-known methods.
* Calculate the resistance (and even co-resistance) of microbial isolates with the `portion_R`, `portion_IR`, `portion_I`, `portion_SI` and `portion_S` functions, that can also be used with the `dplyr` package (e.g. in conjunction with `summarise`)
* Plot AMR results with `geom_rsi`, a function made for the `ggplot2` package
* Predict antimicrobial resistance for the nextcoming years using logistic regression models with the `resistance_predict` function
* Conduct descriptive statistics to enhance base R: calculate kurtosis, skewness and create frequency tables
4. It **teaches the user** how to use all the above actions, by showing many examples in the help pages. The package contains an example data set called `septic_patients`. This data set, consisting of 2000 blood culture isolates from anonymised septic patients between 2001 and 2017 in the Northern Netherlands, is real and genuine data.
## How to get it?
All versions of this package [are published on CRAN](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR), the official R network with a peer-reviewed submission process.
### Install from CRAN
[](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR) [](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR)
(Note: Downloads measured only by [cran.rstudio.com](https://cran.rstudio.com/package=AMR), this excludes e.g. the official [cran.r-project.org](https://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR))
-
## Contents
* [Why this package?](#why-this-package)
* [How to get it?](#how-to-get-it)
* [Install from CRAN](#install-from-cran)
* [Install from GitHub](#install-from-github)
* [How to use it?](#how-to-use-it)
* [New classes](#new-classes)
* [Overwrite/force resistance based on EUCAST rules](#overwriteforce-resistance-based-on-eucast-rules)
* [Other (microbial) epidemiological functions](#other-microbial-epidemiological-functions)
* [Frequency tables](#frequency-tables)
* [Data sets included in package](#data-sets-included-in-package)
* [Copyright](#copyright)
## Why this package?
This R package was intended to make microbial epidemiology easier. Most functions contain extensive help pages to get started.
This `AMR` package basically does four important things:
1. It **cleanses existing data**, by transforming it to reproducible and profound *classes*, making the most efficient use of R. These function all use artificial intelligence to get expected results:
* Use `as.bactid` to get an ID of a microorganism. It takes almost any text as input that looks like the name or code of a microorganism like "E. coli", "esco" and "esccol". Moreover, it can group all coagulase negative and positive *Staphylococci*, and can transform *Streptococci* into Lancefield groups. This package has a database of ~2500 different (potential) human pathogenic microorganisms.
* Use `as.rsi` to transform values to valid antimicrobial results. It produces just S, I or R based on your input and warns about invalid values. Even values like "<=0.002; S" (combined MIC/RSI) will result in "S".
* Use `as.mic` to cleanse your MIC values. It produces a so-called factor (in SPSS calls this *ordinal*) with valid MIC values as levels. A value like "<=0.002; S" (combined MIC/RSI) will result in "<=0.002".
* Use `as.atc` to get the ATC code of an antibiotic as defined by the WHO. This package contains a database with most LIS codes, official names, DDDs and even trade names of antibiotics. For example, the values "Furabid", "Furadantine", "nitro" will return the ATC code of Nitrofurantoine.
2. It **enhances existing data** and **adds new data** from data sets included in this package.
* Use `EUCAST_rules` to apply [EUCAST expert rules to isolates](http://www.eucast.org/expert_rules_and_intrinsic_resistance/).
* Use `MDRO` (abbreviation of Multi Drug Resistant Organisms) to check your isolates for exceptional resistance with country-specific guidelines with or EUCAST rules. Currently, national guidelines for Germany and the Netherlands are supported.
* Data set `microorganisms` contains the family, genus, species, subspecies, colloqual name and Gram stain of almost 2500 microorganisms. This enables e.g. resistance analysis of different antibiotics per Gram stain.
* Data set `antibiotics` contains the ATC code, LIS codes, official name, trivial name, trade name and DDD of both oral and parenteral administration.
* Use `first_isolate` to identify the first isolates of every patient [using guidelines from the CLSI](https://clsi.org/standards/products/microbiology/documents/m39/) (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute). * You can also identify first *weighted* isolates of every patient, an adjusted version of the CLSI guideline. This takes into account key antibiotics of every strain and compares them.
3. It **analyses the data** with convenient functions that use well-known methods.
* Calculate the resistance (and even co-resistance) of microbial isolates with the `portion_R`, `portion_IR`, `portion_I`, `portion_SI` and `portion_S` functions, that can also be used with the `dplyr` package (e.g. in conjunction with `summarise`)
* Plot AMR results with `geom_rsi`, a function made for the `ggplot2` package
* Predict antimicrobial resistance for the nextcoming years using logistic regression models with the `resistance_predict` function
* Conduct descriptive statistics to enhance base R: calculate kurtosis, skewness and create frequency tables
4. It **teaches the user** how to use all the above actions, by showing many examples in the help pages. The package contains an example data set called `septic_patients`. This data set, consisting of 2000 blood culture isolates from anonymised septic patients between 2001 and 2017 in the Northern Netherlands, is real and genuine data.
## How to get it?
All versions of this package [are published on CRAN](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR), the official R network with a peer-reviewed submission process.
### Install from CRAN
[](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR) [](http://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR)
(Note: Downloads measured only by [cran.rstudio.com](https://cran.rstudio.com/package=AMR), this excludes e.g. the official [cran.r-project.org](https://cran.r-project.org/package=AMR))
-