Use this function to determine a valid microorganism code (mo). Determination is done using intelligent rules and the complete taxonomic kingdoms Bacteria, Chromista, Protozoa, Archaea and most microbial species from the kingdom Fungi (see Source). The input can be almost anything: a full name (like "Staphylococcus aureus"), an abbreviated name (such as "S. aureus"), an abbreviation known in the field (such as "MRSA"), or just a genus. See Examples.
as.mo(
x,
Becker = FALSE,
Lancefield = FALSE,
allow_uncertain = TRUE,
reference_df = get_mo_source(),
ignore_pattern = getOption("AMR_ignore_pattern"),
language = get_AMR_locale(),
info = interactive(),
...
)
is.mo(x)
mo_failures()
mo_uncertainties()
mo_renamed()Arguments
- x
a character vector or a data.frame with one or two columns
- Becker
a logical to indicate whether staphylococci should be categorised into coagulase-negative staphylococci ("CoNS") and coagulase-positive staphylococci ("CoPS") instead of their own species, according to Karsten Becker et al. (1,2,3).
This excludes Staphylococcus aureus at default, use
Becker = "all"to also categorise S. aureus as "CoPS".- Lancefield
a logical to indicate whether a beta-haemolytic Streptococcus should be categorised into Lancefield groups instead of their own species, according to Rebecca C. Lancefield (4). These streptococci will be categorised in their first group, e.g. Streptococcus dysgalactiae will be group C, although officially it was also categorised into groups G and L.
This excludes enterococci at default (who are in group D), use
Lancefield = "all"to also categorise all enterococci as group D.- allow_uncertain
a number between
0(or"none") and3(or"all"), orTRUE(=2) orFALSE(=0) to indicate whether the input should be checked for less probable results, see Details- reference_df
a data.frame to be used for extra reference when translating
xto a validmo. Seeset_mo_source()andget_mo_source()to automate the usage of your own codes (e.g. used in your analysis or organisation).- ignore_pattern
a regular expression (case-insensitive) of which all matches in
xmust returnNA. This can be convenient to exclude known non-relevant input and can also be set with the optionAMR_ignore_pattern, e.g.options(AMR_ignore_pattern = "(not reported|contaminated flora)").- language
language to translate text like "no growth", which defaults to the system language (see
get_AMR_locale())- info
a logical to indicate if a progress bar should be printed if more than 25 items are to be coerced, defaults to
TRUEonly in interactive mode- ...
other arguments passed on to functions
Details
General Info
A microorganism (MO) code from this package (class: mo) is human readable and typically looks like these examples:
Code Full name
--------------- --------------------------------------
B_KLBSL Klebsiella
B_KLBSL_PNMN Klebsiella pneumoniae
B_KLBSL_PNMN_RHNS Klebsiella pneumoniae rhinoscleromatis
| | | |
| | | |
| | | \---> subspecies, a 4-5 letter acronym
| | \----> species, a 4-5 letter acronym
| \----> genus, a 5-7 letter acronym
\----> taxonomic kingdom: A (Archaea), AN (Animalia), B (Bacteria),
C (Chromista), F (Fungi), P (Protozoa)
Values that cannot be coerced will be considered 'unknown' and will get the MO code UNKNOWN.
Use the mo_* functions to get properties based on the returned code, see Examples.
The algorithm uses data from the Catalogue of Life (see below) and from one other source (see microorganisms).
The as.mo() function uses several coercion rules for fast and logical results. It assesses the input matching criteria in the following order:
Human pathogenic prevalence: the function starts with more prevalent microorganisms, followed by less prevalent ones;
Taxonomic kingdom: the function starts with determining Bacteria, then Fungi, then Protozoa, then others;
Breakdown of input values to identify possible matches.
This will lead to the effect that e.g. "E. coli" (a microorganism highly prevalent in humans) will return the microbial ID of Escherichia coli and not Entamoeba coli (a microorganism less prevalent in humans), although the latter would alphabetically come first.
Coping with Uncertain Results
In addition, the as.mo() function can differentiate four levels of uncertainty to guess valid results:
Uncertainty level 0: no additional rules are applied;
Uncertainty level 1: allow previously accepted (but now invalid) taxonomic names and minor spelling errors;
Uncertainty level 2: allow all of level 1, strip values between brackets, inverse the words of the input, strip off text elements from the end keeping at least two elements;
Uncertainty level 3: allow all of level 1 and 2, strip off text elements from the end, allow any part of a taxonomic name.
The level of uncertainty can be set using the argument allow_uncertain. The default is allow_uncertain = TRUE, which is equal to uncertainty level 2. Using allow_uncertain = FALSE is equal to uncertainty level 0 and will skip all rules. You can also use e.g. as.mo(..., allow_uncertain = 1) to only allow up to level 1 uncertainty.
With the default setting (allow_uncertain = TRUE, level 2), below examples will lead to valid results:
"Streptococcus group B (known as S. agalactiae)". The text between brackets will be removed and a warning will be thrown that the result Streptococcus group B (B_STRPT_GRPB) needs review."S. aureus - please mind: MRSA". The last word will be stripped, after which the function will try to find a match. If it does not, the second last word will be stripped, etc. Again, a warning will be thrown that the result Staphylococcus aureus (B_STPHY_AURS) needs review."Fluoroquinolone-resistant Neisseria gonorrhoeae". The first word will be stripped, after which the function will try to find a match. A warning will be thrown that the result Neisseria gonorrhoeae (B_NESSR_GNRR) needs review.
There are three helper functions that can be run after using the as.mo() function:
Use
mo_uncertainties()to get a data.frame that prints in a pretty format with all taxonomic names that were guessed. The output contains the matching score for all matches (see Matching Score for Microorganisms below).Use
mo_failures()to get a character vector with all values that could not be coerced to a valid value.Use
mo_renamed()to get a data.frame with all values that could be coerced based on old, previously accepted taxonomic names.
Microbial Prevalence of Pathogens in Humans
The intelligent rules consider the prevalence of microorganisms in humans grouped into three groups, which is available as the prevalence columns in the microorganisms and microorganisms.old data sets. The grouping into human pathogenic prevalence is explained in the section Matching Score for Microorganisms below.
Source
Becker K et al. Coagulase-Negative Staphylococci. 2014. Clin Microbiol Rev. 27(4): 870-926; doi: 10.1128/CMR.00109-13
Becker K et al. Implications of identifying the recently defined members of the S. aureus complex, S. argenteus and S. schweitzeri: A position paper of members of the ESCMID Study Group for staphylococci and Staphylococcal Diseases (ESGS). 2019. Clin Microbiol Infect; doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2019.02.028
Becker K et al. Emergence of coagulase-negative staphylococci 2020. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 18(4):349-366; doi: 10.1080/14787210.2020.1730813
Lancefield RC A serological differentiation of human and other groups of hemolytic streptococci. 1933. J Exp Med. 57(4): 571-95; doi: 10.1084/jem.57.4.571
Catalogue of Life: 2019 Annual Checklist, http://www.catalogueoflife.org
List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (5 October 2021), doi: 10.1099/ijsem.0.004332
US Edition of SNOMED CT from 1 September 2020, retrieved from the Public Health Information Network Vocabulary Access and Distribution System (PHIN VADS), OID 2.16.840.1.114222.4.11.1009, version 12; url: https://phinvads.cdc.gov/vads/ViewValueSet.action?oid=2.16.840.1.114222.4.11.1009
Stable Lifecycle
The lifecycle of this function is stable. In a stable function, major changes are unlikely. This means that the unlying code will generally evolve by adding new arguments; removing arguments or changing the meaning of existing arguments will be avoided.
If the unlying code needs breaking changes, they will occur gradually. For example, an argument will be deprecated and first continue to work, but will emit an message informing you of the change. Next, typically after at least one newly released version on CRAN, the message will be transformed to an error.
Matching Score for Microorganisms
With ambiguous user input in as.mo() and all the mo_* functions, the returned results are chosen based on their matching score using mo_matching_score(). This matching score \(m\), is calculated as:
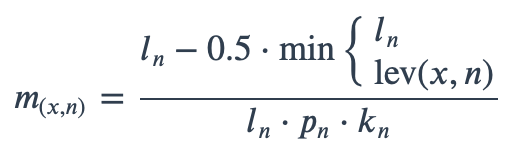
where:
x is the user input;
n is a taxonomic name (genus, species, and subspecies);
ln is the length of n;
lev is the Levenshtein distance function, which counts any insertion, deletion and substitution as 1 that is needed to change x into n;
pn is the human pathogenic prevalence group of n, as described below;
kn is the taxonomic kingdom of n, set as Bacteria = 1, Fungi = 2, Protozoa = 3, Archaea = 4, others = 5.
The grouping into human pathogenic prevalence (\(p\)) is based on experience from several microbiological laboratories in the Netherlands in conjunction with international reports on pathogen prevalence. Group 1 (most prevalent microorganisms) consists of all microorganisms where the taxonomic class is Gammaproteobacteria or where the taxonomic genus is Enterococcus, Staphylococcus or Streptococcus. This group consequently contains all common Gram-negative bacteria, such as Pseudomonas and Legionella and all species within the order Enterobacterales. Group 2 consists of all microorganisms where the taxonomic phylum is Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria or Sarcomastigophora, or where the taxonomic genus is Absidia, Acremonium, Actinotignum, Alternaria, Anaerosalibacter, Apophysomyces, Arachnia, Aspergillus, Aureobacterium, Aureobasidium, Bacteroides, Basidiobolus, Beauveria, Blastocystis, Branhamella, Calymmatobacterium, Candida, Capnocytophaga, Catabacter, Chaetomium, Chryseobacterium, Chryseomonas, Chrysonilia, Cladophialophora, Cladosporium, Conidiobolus, Cryptococcus, Curvularia, Exophiala, Exserohilum, Flavobacterium, Fonsecaea, Fusarium, Fusobacterium, Hendersonula, Hypomyces, Koserella, Lelliottia, Leptosphaeria, Leptotrichia, Malassezia, Malbranchea, Mortierella, Mucor, Mycocentrospora, Mycoplasma, Nectria, Ochroconis, Oidiodendron, Phoma, Piedraia, Pithomyces, Pityrosporum, Prevotella, Pseudallescheria, Rhizomucor, Rhizopus, Rhodotorula, Scolecobasidium, Scopulariopsis, Scytalidium, Sporobolomyces, Stachybotrys, Stomatococcus, Treponema, Trichoderma, Trichophyton, Trichosporon, Tritirachium or Ureaplasma. Group 3 consists of all other microorganisms.
All characters in \(x\) and \(n\) are ignored that are other than A-Z, a-z, 0-9, spaces and parentheses.
All matches are sorted descending on their matching score and for all user input values, the top match will be returned. This will lead to the effect that e.g., "E. coli" will return the microbial ID of Escherichia coli (\(m = 0.688\), a highly prevalent microorganism found in humans) and not Entamoeba coli (\(m = 0.079\), a less prevalent microorganism in humans), although the latter would alphabetically come first.
Since AMR version 1.8.1, common microorganism abbreviations are ignored in determining the matching score. These abbreviations are currently: AIEC, ATEC, BORSA, CRSM, DAEC, EAEC, EHEC, EIEC, EPEC, ETEC, GISA, MRPA, MRSA, MRSE, MSSA, MSSE, NMEC, PISP, PRSP, STEC, UPEC, VISA, VISP, VRE, VRSA and VRSP.
Catalogue of Life
![]()
This package contains the complete taxonomic tree of almost all microorganisms (~71,000 species) from the authoritative and comprehensive Catalogue of Life (CoL, http://www.catalogueoflife.org). The CoL is the most comprehensive and authoritative global index of species currently available. Nonetheless, we supplemented the CoL data with data from the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN, lpsn.dsmz.de). This supplementation is needed until the CoL+ project is finished, which we await.
Click here for more information about the included taxa. Check which versions of the CoL and LPSN were included in this package with catalogue_of_life_version().
Reference Data Publicly Available
All reference data sets (about microorganisms, antibiotics, R/SI interpretation, EUCAST rules, etc.) in this AMR package are publicly and freely available. We continually export our data sets to formats for use in R, SPSS, SAS, Stata and Excel. We also supply flat files that are machine-readable and suitable for input in any software program, such as laboratory information systems. Please find all download links on our website, which is automatically updated with every code change.
Read more on Our Website!
On our website https://msberends.github.io/AMR/ you can find a comprehensive tutorial about how to conduct AMR data analysis, the complete documentation of all functions and an example analysis using WHONET data.
See also
microorganisms for the data.frame that is being used to determine ID's.
The mo_* functions (such as mo_genus(), mo_gramstain()) to get properties based on the returned code.
Examples
# \donttest{
# These examples all return "B_STPHY_AURS", the ID of S. aureus:
as.mo("sau") # WHONET code
as.mo("stau")
as.mo("STAU")
as.mo("staaur")
as.mo("S. aureus")
as.mo("S aureus")
as.mo("Staphylococcus aureus")
as.mo("Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)")
as.mo("Zthafilokkoockus oureuz") # handles incorrect spelling
as.mo("MRSA") # Methicillin Resistant S. aureus
as.mo("VISA") # Vancomycin Intermediate S. aureus
as.mo("VRSA") # Vancomycin Resistant S. aureus
as.mo(115329001) # SNOMED CT code
# Dyslexia is no problem - these all work:
as.mo("Ureaplasma urealyticum")
as.mo("Ureaplasma urealyticus")
as.mo("Ureaplasmium urealytica")
as.mo("Ureaplazma urealitycium")
as.mo("Streptococcus group A")
as.mo("GAS") # Group A Streptococci
as.mo("GBS") # Group B Streptococci
as.mo("S. epidermidis") # will remain species: B_STPHY_EPDR
as.mo("S. epidermidis", Becker = TRUE) # will not remain species: B_STPHY_CONS
as.mo("S. pyogenes") # will remain species: B_STRPT_PYGN
as.mo("S. pyogenes", Lancefield = TRUE) # will not remain species: B_STRPT_GRPA
# All mo_* functions use as.mo() internally too (see ?mo_property):
mo_genus("E. coli") # returns "Escherichia"
mo_gramstain("E. coli") # returns "Gram negative"
mo_is_intrinsic_resistant("E. coli", "vanco") # returns TRUE
# }