These functions can be used for generating random MIC values and disk diffusion diameters, for AMR data analysis practice. By providing a microorganism and antimicrobial drug, the generated results will reflect reality as much as possible.
Usage
random_mic(size = NULL, mo = NULL, ab = NULL, skew = "right",
severity = 1, ...)
random_disk(size = NULL, mo = NULL, ab = NULL, skew = "left",
severity = 1, ...)
random_sir(size = NULL, prob_SIR = c(0.33, 0.33, 0.33), ...)Arguments
- size
Desired size of the returned vector. If used in a data.frame call or
dplyrverb, will get the current (group) size if left blank.- mo
Any character that can be coerced to a valid microorganism code with
as.mo(). Can be the same length assize.- ab
Any character that can be coerced to a valid antimicrobial drug code with
as.ab().- skew
Direction of skew for MIC or disk values, either
"right"or"left". A left-skewed distribution has the majority of the data on the right.- severity
Skew severity; higher values will increase the skewedness. Default is
2; use0to prevent skewedness.- ...
Ignored, only in place to allow future extensions.
- prob_SIR
A vector of length 3: the probabilities for "S" (1st value), "I" (2nd value) and "R" (3rd value).
Details
Internally, MIC and disk zone values are sampled based on clinical breakpoints defined in the clinical_breakpoints data set. To create specific generated values per bug or drug, set the mo and/or ab argument. The MICs are sampled on a log2 scale and disks linearly, using weighted probabilities. The weights are based on the skew and severity arguments:
skew = "right"places more emphasis on lower MIC or higher disk values.skew = "left"places more emphasis on higher MIC or lower disk values.severitycontrols the exponential bias applied.
Examples
random_mic(25)
#> Class 'mic'
#> [1] 0.125 2 16 1 0.004 0.008 0.0005 0.125
#> [9] 2 0.008 0.008 0.016 0.064 0.064 <=0.0002 0.001
#> [17] 0.0005 0.5 0.002 0.002 0.125 8 <=0.0002 0.002
#> [25] 0.064
random_disk(25)
#> Class 'disk'
#> [1] 47 24 47 38 28 36 33 31 50 41 29 40 31 44 45 37 40 44 49 9 48 20 37 47 28
random_sir(25)
#> Class 'sir'
#> [1] S R R S S I S I S S I S R I I I I S I R I I I I R
# add more skewedness, make more realistic by setting a bug and/or drug:
disks <- random_disk(100, severity = 2, mo = "Escherichia coli", ab = "CIP")
plot(disks)
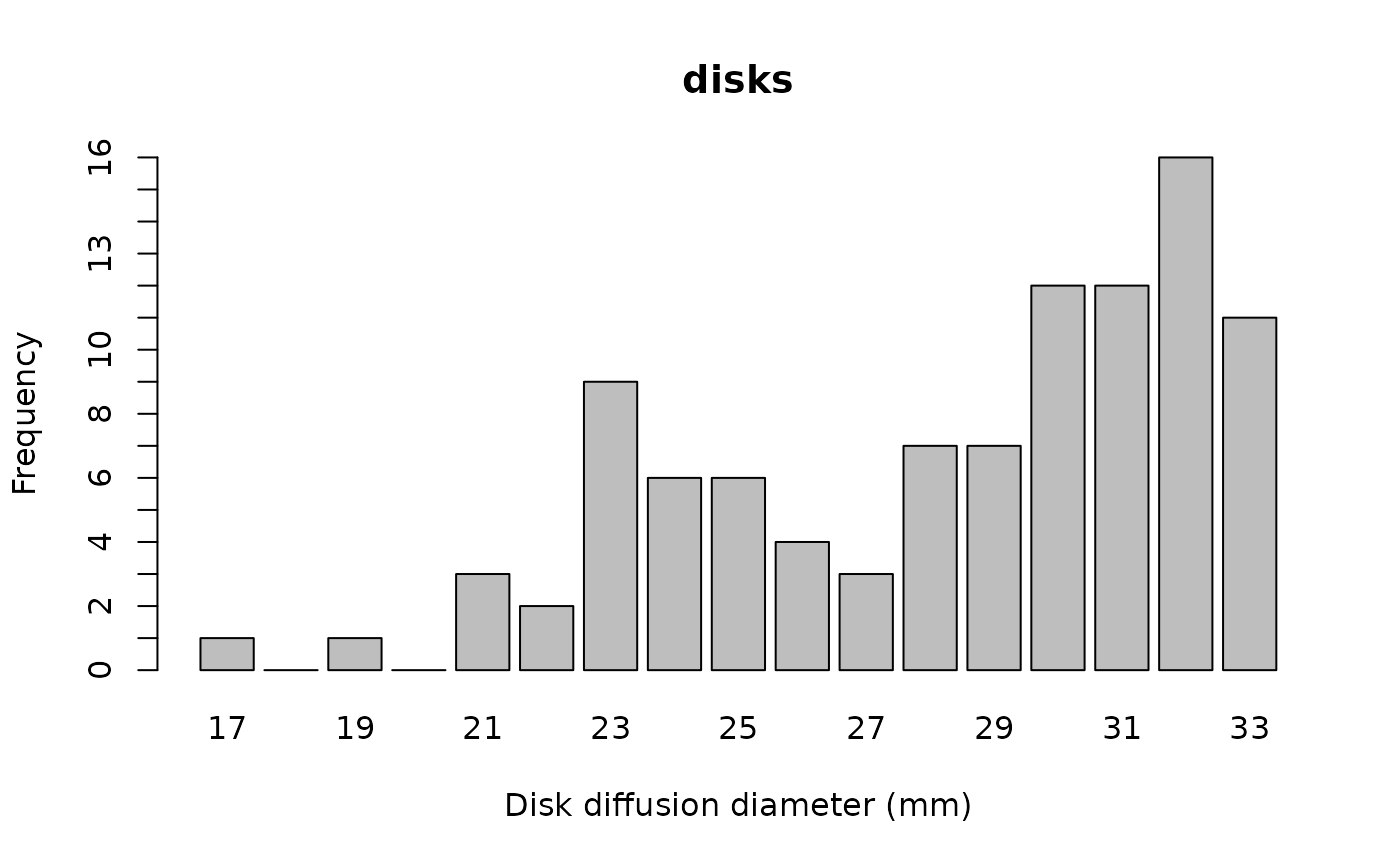 # `plot()` and `ggplot2::autoplot()` allow for coloured bars if `mo` and `ab` are set
plot(disks, mo = "Escherichia coli", ab = "CIP", guideline = "CLSI 2025")
# `plot()` and `ggplot2::autoplot()` allow for coloured bars if `mo` and `ab` are set
plot(disks, mo = "Escherichia coli", ab = "CIP", guideline = "CLSI 2025")
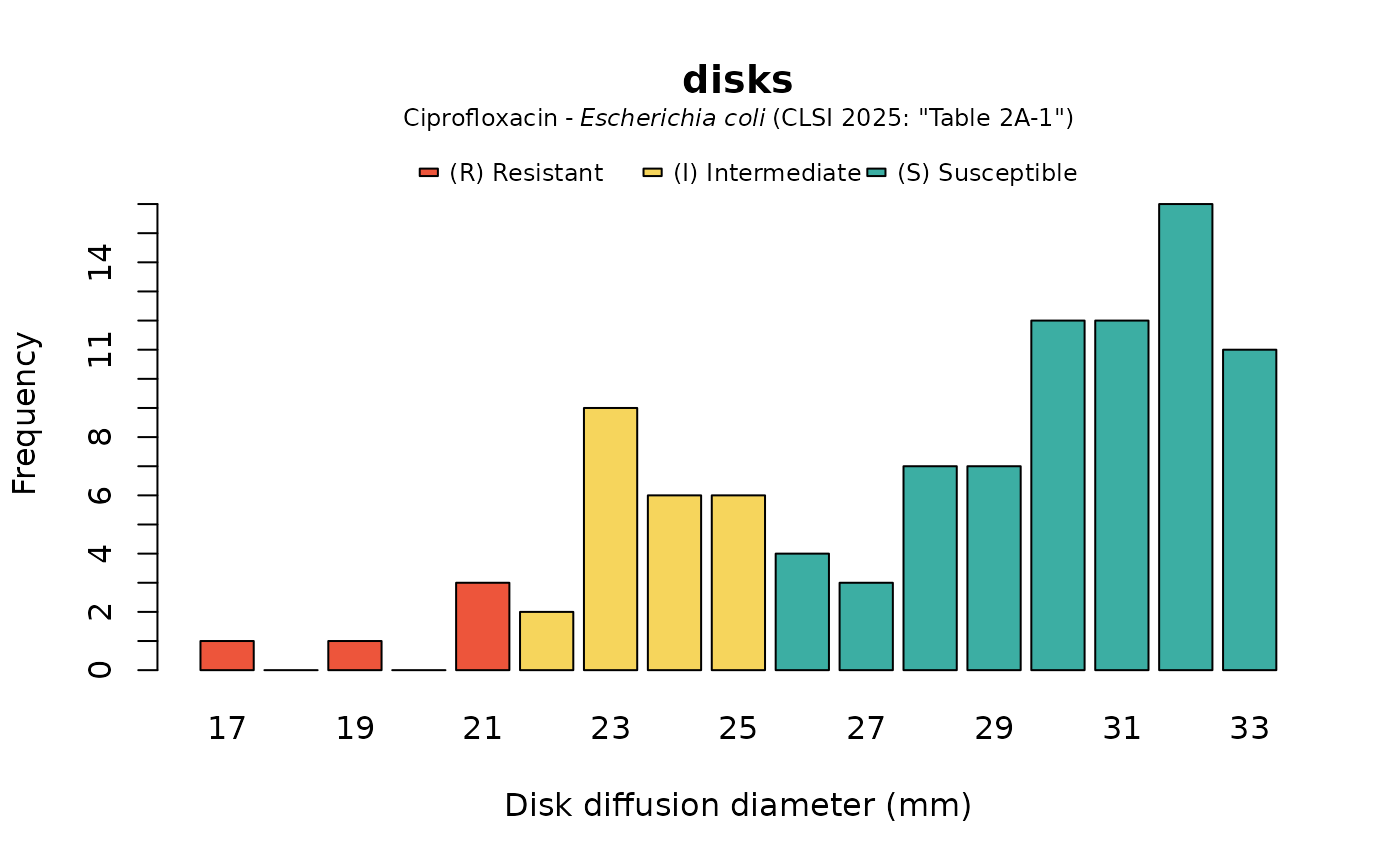 # \donttest{
random_mic(25, "Klebsiella pneumoniae") # range 0.0625-64
#> Class 'mic'
#> [1] 0.0005 8 0.008 0.0002 0.0002 0.0002 0.0002 <=0.0001
#> [9] 64 <=0.0001 1 0.5 0.001 0.5 0.001 0.0005
#> [17] 0.016 0.008 0.002 0.032 <=0.0001 0.0002 0.001 0.0005
#> [25] 0.001
random_mic(25, "Klebsiella pneumoniae", "meropenem") # range 0.0625-16
#> Class 'mic'
#> [1] <=0.5 <=0.5 2 <=0.5 1 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 1 <=0.5 <=0.5
#> [13] <=0.5 1 <=0.5 1 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 2 1
#> [25] 2
random_mic(25, "Streptococcus pneumoniae", "meropenem") # range 0.0625-4
#> Class 'mic'
#> [1] 0.125 0.125 1 0.25 0.5 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125
#> [13] 1 0.125 0.5 1 0.125 0.25 0.5 0.25 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.125
#> [25] 0.25
random_disk(25, "Klebsiella pneumoniae") # range 8-50
#> Class 'disk'
#> [1] 32 21 23 21 14 22 25 29 29 28 34 34 34 33 13 28 33 34 32 25 18 26 13 21 33
random_disk(25, "Klebsiella pneumoniae", "ampicillin") # range 11-17
#> Class 'disk'
#> [1] 20 21 15 22 16 22 16 14 21 17 15 19 20 17 18 21 16 20 11 22 19 18 19 11 21
random_disk(25, "Streptococcus pneumoniae", "ampicillin") # range 12-27
#> Class 'disk'
#> [1] 29 25 31 17 29 21 31 34 33 31 29 30 23 20 33 20 34 32 35 26 26 26 34 30 33
# }
# \donttest{
random_mic(25, "Klebsiella pneumoniae") # range 0.0625-64
#> Class 'mic'
#> [1] 0.0005 8 0.008 0.0002 0.0002 0.0002 0.0002 <=0.0001
#> [9] 64 <=0.0001 1 0.5 0.001 0.5 0.001 0.0005
#> [17] 0.016 0.008 0.002 0.032 <=0.0001 0.0002 0.001 0.0005
#> [25] 0.001
random_mic(25, "Klebsiella pneumoniae", "meropenem") # range 0.0625-16
#> Class 'mic'
#> [1] <=0.5 <=0.5 2 <=0.5 1 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 1 <=0.5 <=0.5
#> [13] <=0.5 1 <=0.5 1 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 <=0.5 2 1
#> [25] 2
random_mic(25, "Streptococcus pneumoniae", "meropenem") # range 0.0625-4
#> Class 'mic'
#> [1] 0.125 0.125 1 0.25 0.5 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125 0.125
#> [13] 1 0.125 0.5 1 0.125 0.25 0.5 0.25 0.5 0.5 0.5 0.125
#> [25] 0.25
random_disk(25, "Klebsiella pneumoniae") # range 8-50
#> Class 'disk'
#> [1] 32 21 23 21 14 22 25 29 29 28 34 34 34 33 13 28 33 34 32 25 18 26 13 21 33
random_disk(25, "Klebsiella pneumoniae", "ampicillin") # range 11-17
#> Class 'disk'
#> [1] 20 21 15 22 16 22 16 14 21 17 15 19 20 17 18 21 16 20 11 22 19 18 19 11 21
random_disk(25, "Streptococcus pneumoniae", "ampicillin") # range 12-27
#> Class 'disk'
#> [1] 29 25 31 17 29 21 31 34 33 31 29 30 23 20 33 20 34 32 35 26 26 26 34 30 33
# }