How to predict antimicrobial resistance
Source:vignettes/resistance_predict.Rmd
resistance_predict.RmdNeeded R packages
As with many uses in R, we need some additional packages for AMR data analysis. Our package works closely together with the tidyverse packages dplyr and ggplot2 by Dr Hadley Wickham. The tidyverse tremendously improves the way we conduct data science - it allows for a very natural way of writing syntaxes and creating beautiful plots in R.
Our AMR package depends on these packages and even extends their use and functions.
Prediction analysis
Our package contains a function resistance_predict(), which takes the same input as functions for other AMR data analysis. Based on a date column, it calculates cases per year and uses a regression model to predict antimicrobial resistance.
It is basically as easy as:
# resistance prediction of piperacillin/tazobactam (TZP):
resistance_predict(tbl = example_isolates, col_date = "date", col_ab = "TZP", model = "binomial")
# or:
example_isolates %>%
resistance_predict(col_ab = "TZP",
model "binomial")
# to bind it to object 'predict_TZP' for example:
predict_TZP <- example_isolates %>%
resistance_predict(col_ab = "TZP",
model = "binomial")The function will look for a date column itself if col_date is not set.
When running any of these commands, a summary of the regression model will be printed unless using resistance_predict(..., info = FALSE).
# ℹ Using column 'date' as input for `col_date`.This text is only a printed summary - the actual result (output) of the function is a data.frame containing for each year: the number of observations, the actual observed resistance, the estimated resistance and the standard error below and above the estimation:
predict_TZP
# year value se_min se_max observations observed estimated
# 1 2002 0.20000000 NA NA 15 0.20000000 0.05616378
# 2 2003 0.06250000 NA NA 32 0.06250000 0.06163839
# 3 2004 0.08536585 NA NA 82 0.08536585 0.06760841
# 4 2005 0.05000000 NA NA 60 0.05000000 0.07411100
# 5 2006 0.05084746 NA NA 59 0.05084746 0.08118454
# 6 2007 0.12121212 NA NA 66 0.12121212 0.08886843
# 7 2008 0.04166667 NA NA 72 0.04166667 0.09720264
# 8 2009 0.01639344 NA NA 61 0.01639344 0.10622731
# 9 2010 0.05660377 NA NA 53 0.05660377 0.11598223
# 10 2011 0.18279570 NA NA 93 0.18279570 0.12650615
# 11 2012 0.30769231 NA NA 65 0.30769231 0.13783610
# 12 2013 0.06896552 NA NA 58 0.06896552 0.15000651
# 13 2014 0.10000000 NA NA 60 0.10000000 0.16304829
# 14 2015 0.23636364 NA NA 55 0.23636364 0.17698785
# 15 2016 0.22619048 NA NA 84 0.22619048 0.19184597
# 16 2017 0.16279070 NA NA 86 0.16279070 0.20763675
# 17 2018 0.22436641 0.1938710 0.2548618 NA NA 0.22436641
# 18 2019 0.24203228 0.2062911 0.2777735 NA NA 0.24203228
# 19 2020 0.26062172 0.2191758 0.3020676 NA NA 0.26062172
# 20 2021 0.28011130 0.2325557 0.3276669 NA NA 0.28011130
# 21 2022 0.30046606 0.2464567 0.3544755 NA NA 0.30046606
# 22 2023 0.32163907 0.2609011 0.3823771 NA NA 0.32163907
# 23 2024 0.34357130 0.2759081 0.4112345 NA NA 0.34357130
# 24 2025 0.36619175 0.2914934 0.4408901 NA NA 0.36619175
# 25 2026 0.38941799 0.3076686 0.4711674 NA NA 0.38941799
# 26 2027 0.41315710 0.3244399 0.5018743 NA NA 0.41315710
# 27 2028 0.43730688 0.3418075 0.5328063 NA NA 0.43730688
# 28 2029 0.46175755 0.3597639 0.5637512 NA NA 0.46175755
# 29 2030 0.48639359 0.3782932 0.5944939 NA NA 0.48639359
# 30 2031 0.51109592 0.3973697 0.6248221 NA NA 0.51109592
# 31 2032 0.53574417 0.4169574 0.6545309 NA NA 0.53574417The function plot is available in base R, and can be extended by other packages to depend the output based on the type of input. We extended its function to cope with resistance predictions:
plot(predict_TZP)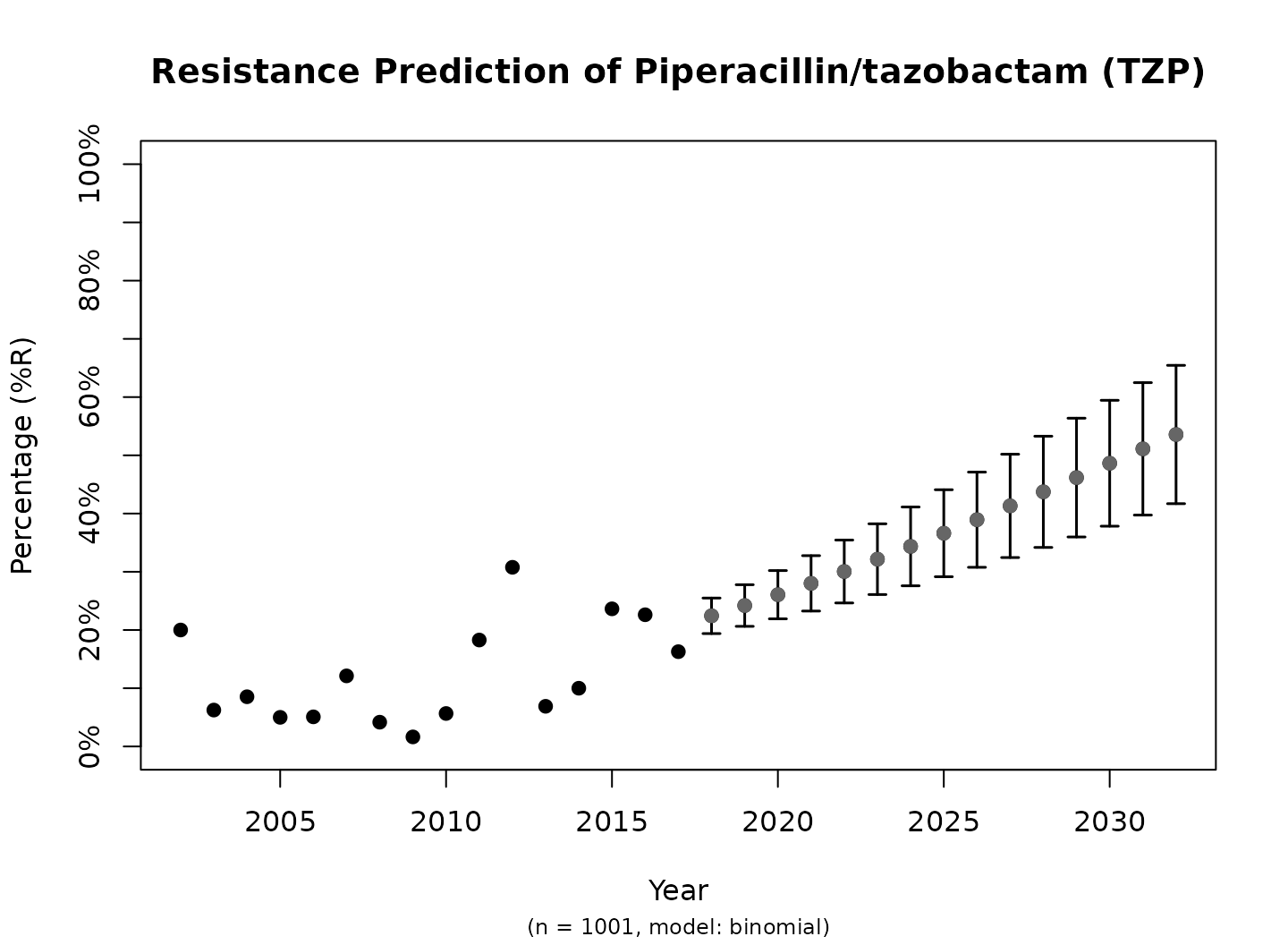
This is the fastest way to plot the result. It automatically adds the right axes, error bars, titles, number of available observations and type of model.
We also support the ggplot2 package with our custom function ggplot_rsi_predict() to create more appealing plots:
ggplot_rsi_predict(predict_TZP)
# choose for error bars instead of a ribbon
ggplot_rsi_predict(predict_TZP, ribbon = FALSE)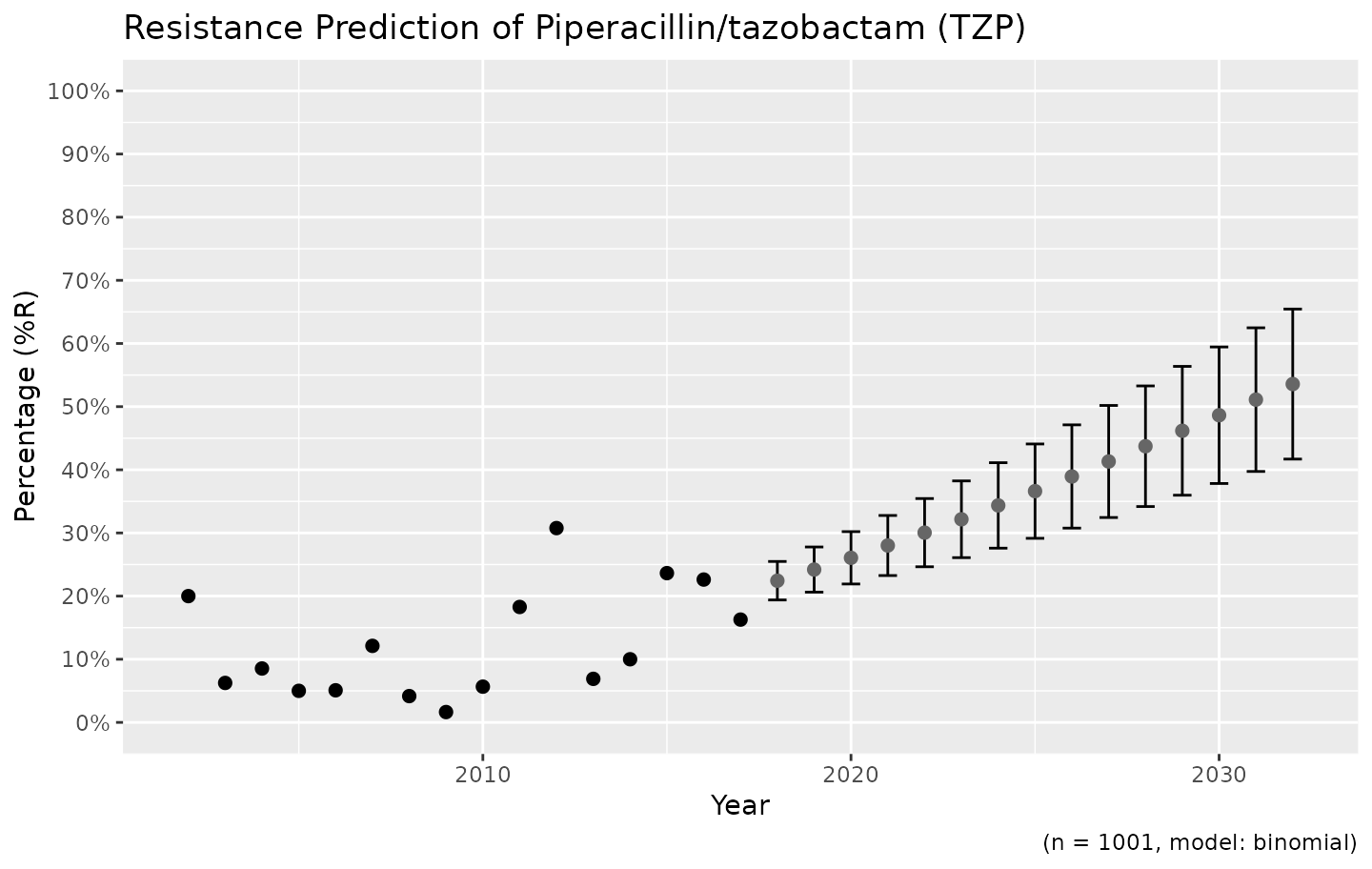
Choosing the right model
Resistance is not easily predicted; if we look at vancomycin resistance in Gram-positive bacteria, the spread (i.e. standard error) is enormous:
example_isolates %>%
filter(mo_gramstain(mo, language = NULL) == "Gram-positive") %>%
resistance_predict(col_ab = "VAN", year_min = 2010, info = FALSE, model = "binomial") %>%
ggplot_rsi_predict()
# ℹ Using column 'date' as input for `col_date`.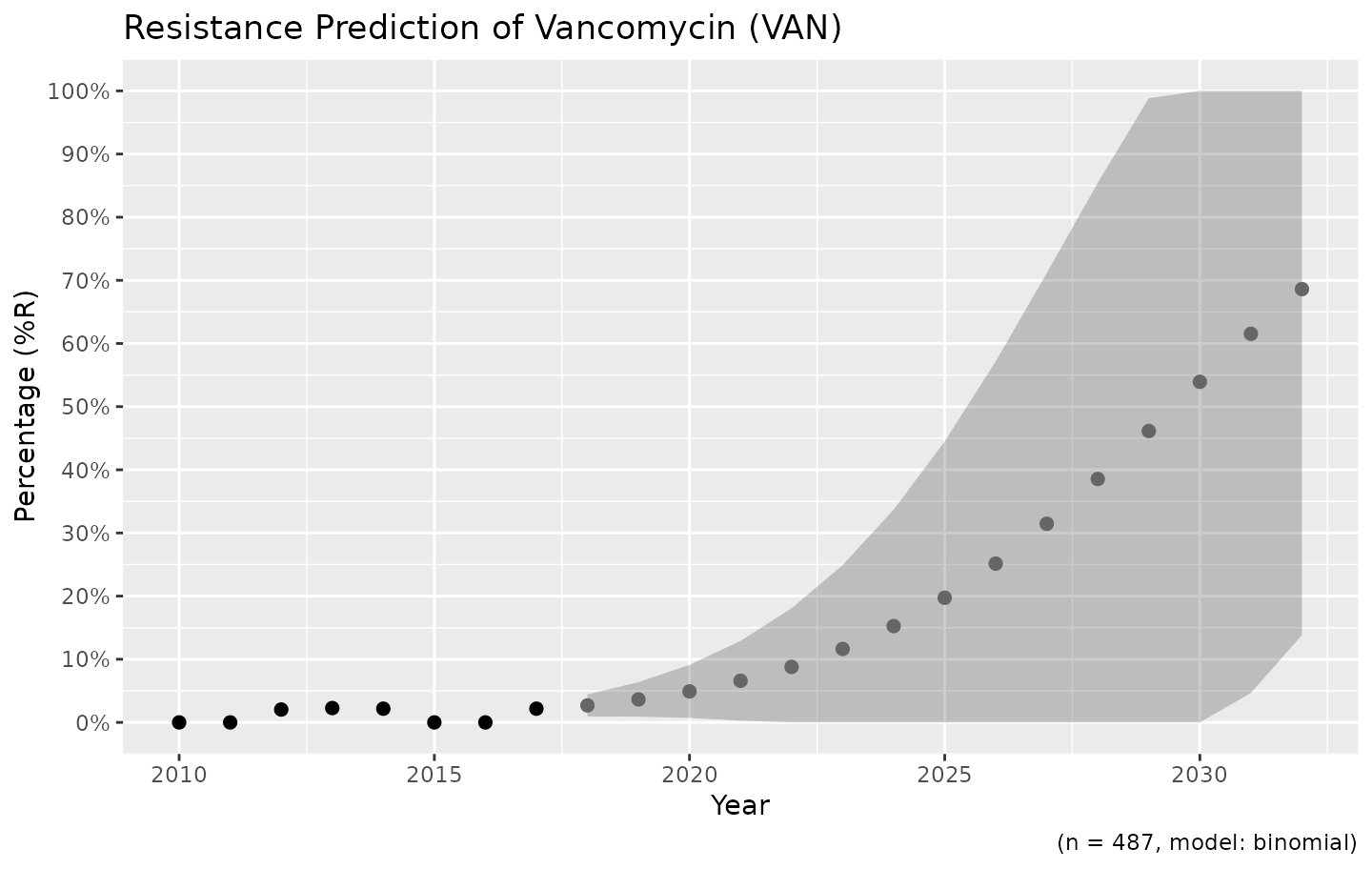
Vancomycin resistance could be 100% in ten years, but might remain very low.
You can define the model with the model parameter. The model chosen above is a generalised linear regression model using a binomial distribution, assuming that a period of zero resistance was followed by a period of increasing resistance leading slowly to more and more resistance.
Valid values are:
| Input values | Function used by R | Type of model |
|---|---|---|
"binomial" or "binom" or "logit"
|
glm(..., family = binomial) |
Generalised linear model with binomial distribution |
"loglin" or "poisson"
|
glm(..., family = poisson) |
Generalised linear model with poisson distribution |
"lin" or "linear"
|
lm() |
Linear model |
For the vancomycin resistance in Gram-positive bacteria, a linear model might be more appropriate:
example_isolates %>%
filter(mo_gramstain(mo, language = NULL) == "Gram-positive") %>%
resistance_predict(col_ab = "VAN", year_min = 2010, info = FALSE, model = "linear") %>%
ggplot_rsi_predict()
# ℹ Using column 'date' as input for `col_date`.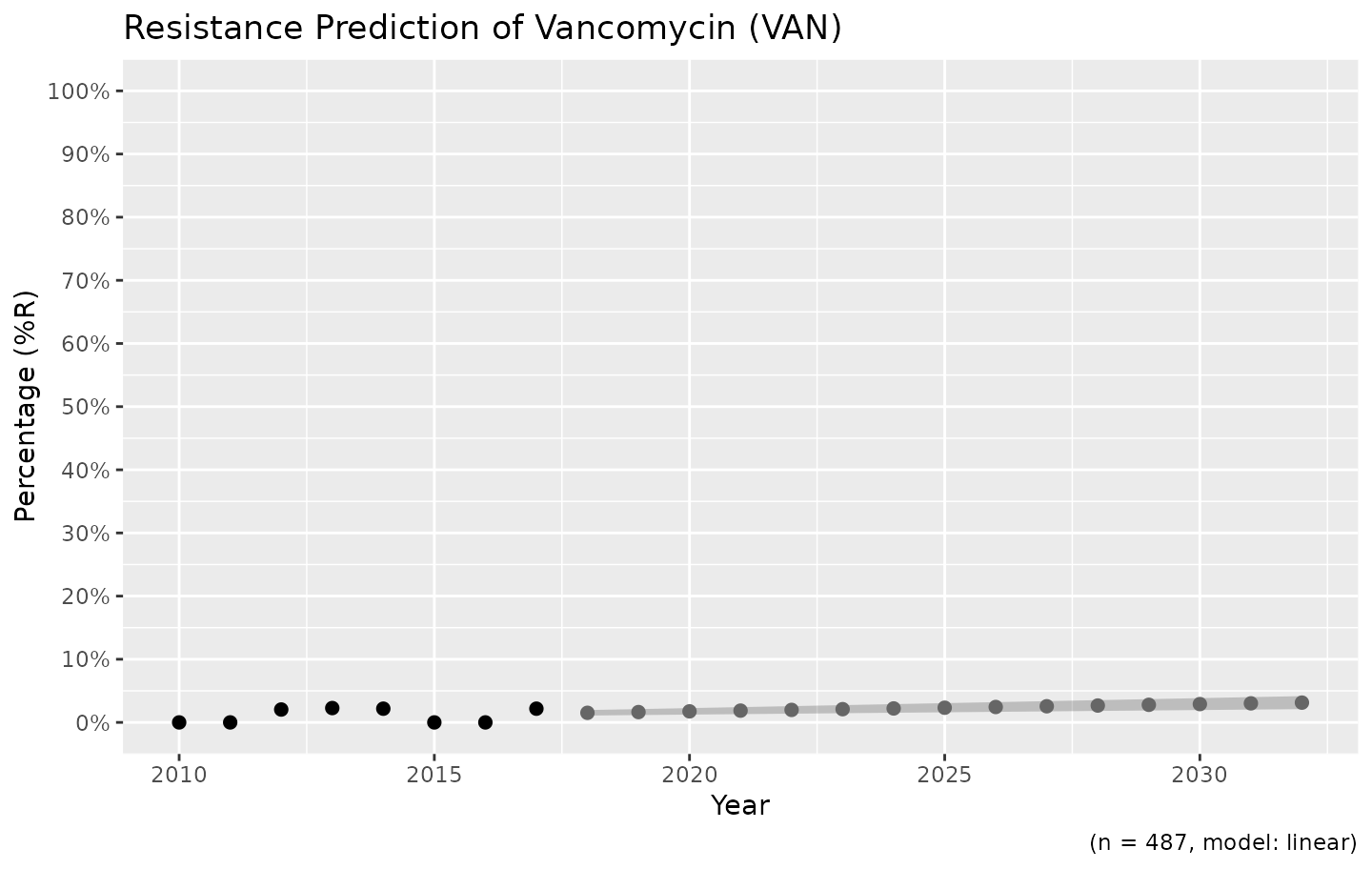
The model itself is also available from the object, as an attribute:
model <- attributes(predict_TZP)$model
summary(model)$family
#
# Family: binomial
# Link function: logit
summary(model)$coefficients
# Estimate Std. Error z value Pr(>|z|)
# (Intercept) -200.67944891 46.17315349 -4.346237 1.384932e-05
# year 0.09883005 0.02295317 4.305725 1.664395e-05