6.2 KiB
AMR
This is an R package to simplify the analysis and prediction of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR).
This R package was created for academic research by PhD students of the Faculty of Medical Sciences of the University of Groningen and the Medical Microbiology & Infection Prevention department of the University Medical Center Groningen (UMCG). They also maintain this package, see Authors.
Why this package?
This R package contains functions to make microbiological, epidemiological data analysis easier. It allows the use of some new S3 classes to work with MIC values and antimicrobial interpretations (i.e. values S, I and R).
AMR can also be predicted for the forthcoming years with the rsi_predict function. For use with the dplyr package, the rsi function can be used in conjunction with summarise to calculate the resistance percentages of different antibiotic columns of a table.
It also contains functions to translate antibiotic codes from the lab (like "AMOX") or the WHO (like "J01CA04") to trivial names (like "amoxicillin") and vice versa.
How to get it?
This package is available on CRAN (latest stable version) and also here on GitHub (latest development version).
Latest stable version from CRAN (recommended)
RStudio:
- Click on
Toolsand thenInstall Packages.. - Type in
AMRand press Install
Other:
install.packages("AMR")
Latest development version from GitHub
devtools::install_github("msberends/AMR")
How to use it?
# Call it with:
library(AMR)
# For a list of functions:
help(package = "AMR")
Overwrite/force resistance based on EUCAST rules
This is also called interpretive reading.
before <- data.frame(bactid = c("STAAUR", # Staphylococcus aureus
"ENCFAE" # Enterococcus faecalis
"ESCCOL", # Escherichia coli
"KLEPNE", # Klebsiella pneumoniae
"PSEAER"), # Pseudomonas aeruginosa
vanc = "-", # Vancomycin
amox = "-", # Amoxicillin
coli = "-", # Colistin
cfta = "-", # Ceftazidime
cfur = "-", # Cefuroxime
stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
before
# bactid vanc amox coli cfta cfur
# 1 STAAUR - - - - -
# 2 ENCFAE - - - - -
# 3 ESCCOL - - - - -
# 4 KLEPNE - - - - -
# 5 PSEAER - - - - -
# Now apply those rules; just need a column with bacteria ID's and antibiotic results:
after <- EUCAST_rules(before)
after
# bactid vanc amox coli cfta cfur
# 1 STAAUR - - R R -
# 2 ENCFAE - - R R R
# 3 ESCCOL R - - - -
# 4 KLEPNE R R - - -
# 5 PSEAER R R - - R
New classes
This package contains two new S3 classes: mic for MIC values (e.g. from Vitek or Phoenix) and rsi for antimicrobial drug interpretations (i.e. S, I and R). Both are actually ordered factors under the hood (an MIC of 2 being higher than <=1 but lower than >=32, and for class rsi factors are ordered as S < I < R).
Both classes have extensions for existing generic functions like print, summary and plot.
# Transform values to new classes
mic_data <- as.mic(c(">=32", "1.0", "8", "<=0.128", "8", "16", "16"))
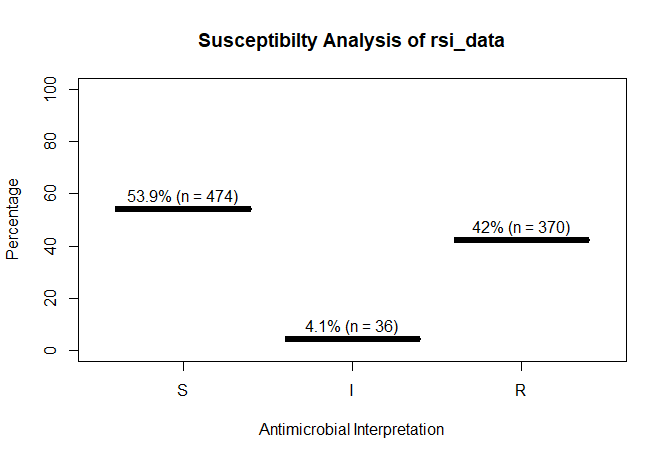
rsi_data <- as.rsi(c(rep("S", 474), rep("I", 36), rep("R", 370)))
These functions also try to coerce valid values.
Quick overviews when just printing objects:
mic_data
# Class 'mic': 7 isolates
#
# <NA> 0
#
# <=0.128 1 8 16 >=32
# 1 1 2 2 1
rsi_data
# Class 'rsi': 880 isolates
#
# <NA>: 0
# Sum of S: 474
# Sum of IR: 406
# - Sum of R: 370
# - Sum of I: 36
#
# %S %IR %I %R
# 53.9 46.1 4.1 42.0
A plot of rsi_data:
plot(rsi_data)
Other epidemiological functions:
# Determine key antibiotic based on bacteria ID
key_antibiotics(...)
# Selection of first isolates of any patient
first_isolate(...)
# Calculate resistance levels of antibiotics, can be used with `summarise` (dplyr)
rsi(...)
# Predict resistance levels of antibiotics
rsi_predict(...)
# Get name of antibiotic by ATC code
abname(...)
abname("J01CR02", from = "atc", to = "umcg") # "AMCL"
Databases included in package
Datasets to work with antibiotics and bacteria properties.
# Dataset with ATC antibiotics codes, official names and DDD's (oral and parenteral)
ablist # A tibble: 420 x 12
# Dataset with bacteria codes and properties like gram stain and aerobic/anaerobic
bactlist # A tibble: 2,507 x 10
Authors
- Berends MS1,2, PhD Student
- Luz CF1, PhD Student
- Hassing EEA2, Data Analyst (contributor)
1 Department of Medical Microbiology, University of Groningen, University Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, the Netherlands
2 Department of Medical, Market and Innovation (MMI), Certe Medische diagnostiek & advies, Groningen, the Netherlands
Copyright
This R package is licensed under the GNU General Public License (GPL) v2.0. In a nutshell, this means that this package:
-
May be used for commercial purposes
-
May be used for private purposes
-
May be modified, although:
- Modifications must be released under the same license when distributing the package
- Changes made to the code must be documented
-
May be distributed, although:
- Source code must be made available when the package is distributed
- A copy of the license and copyright notice must be included with the package.
-
Comes with a LIMITATION of liability
-
Comes with NO warranty