One of the most important features of this package is the complete microbial taxonomic database, supplied by the Catalogue of Life. We created a function as.mo() that transforms any user input value to a valid microbial ID by using intelligent rules combined with the taxonomic tree of Catalogue of Life.
Using the microbenchmark package, we can review the calculation performance of this function. Its function microbenchmark() runs different input expressions independently of each other and measures their time-to-result.
microbenchmark <- microbenchmark::microbenchmark library(AMR) library(dplyr)
In the next test, we try to ‘coerce’ different input values into the microbial code of Staphylococcus aureus. Coercion is a computational process of forcing output based on an input. For microorganism names, coercing user input to taxonomically valid microorganism names is crucial to ensure correct interpretation and to enable grouping based on taxonomic properties.
The actual result is the same every time: it returns its microorganism code B_STPHY_AURS (B stands for Bacteria, the taxonomic kingdom).
But the calculation time differs a lot:
S.aureus <- microbenchmark( as.mo("sau"), # WHONET code as.mo("stau"), as.mo("STAU"), as.mo("staaur"), as.mo("STAAUR"), as.mo("S. aureus"), as.mo("S aureus"), as.mo("Staphylococcus aureus"), # official taxonomic name as.mo("Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)"), # additional text as.mo("Sthafilokkockus aaureuz"), # incorrect spelling as.mo("MRSA"), # Methicillin Resistant S. aureus as.mo("VISA"), # Vancomycin Intermediate S. aureus as.mo("VRSA"), # Vancomycin Resistant S. aureus as.mo(22242419), # Catalogue of Life ID times = 10) print(S.aureus, unit = "ms", signif = 2) # Unit: milliseconds # expr min lq mean median uq max # as.mo("sau") 7.5 9.0 21.0 11.0 37.0 43.0 # as.mo("stau") 130.0 130.0 170.0 170.0 180.0 280.0 # as.mo("STAU") 130.0 140.0 150.0 150.0 170.0 180.0 # as.mo("staaur") 7.3 9.7 13.0 11.0 11.0 37.0 # as.mo("STAAUR") 7.3 9.2 13.0 9.8 10.0 45.0 # as.mo("S. aureus") 10.0 11.0 23.0 12.0 12.0 120.0 # as.mo("S aureus") 9.9 12.0 23.0 13.0 40.0 43.0 # as.mo("Staphylococcus aureus") 5.7 6.4 7.4 7.2 8.8 9.5 # as.mo("Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)") 850.0 860.0 870.0 870.0 880.0 910.0 # as.mo("Sthafilokkockus aaureuz") 330.0 350.0 360.0 360.0 370.0 390.0 # as.mo("MRSA") 7.7 9.2 12.0 9.7 11.0 39.0 # as.mo("VISA") 19.0 21.0 25.0 22.0 24.0 55.0 # as.mo("VRSA") 18.0 22.0 30.0 25.0 26.0 57.0 # as.mo(22242419) 140.0 150.0 170.0 150.0 190.0 210.0 # neval # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10 # 10
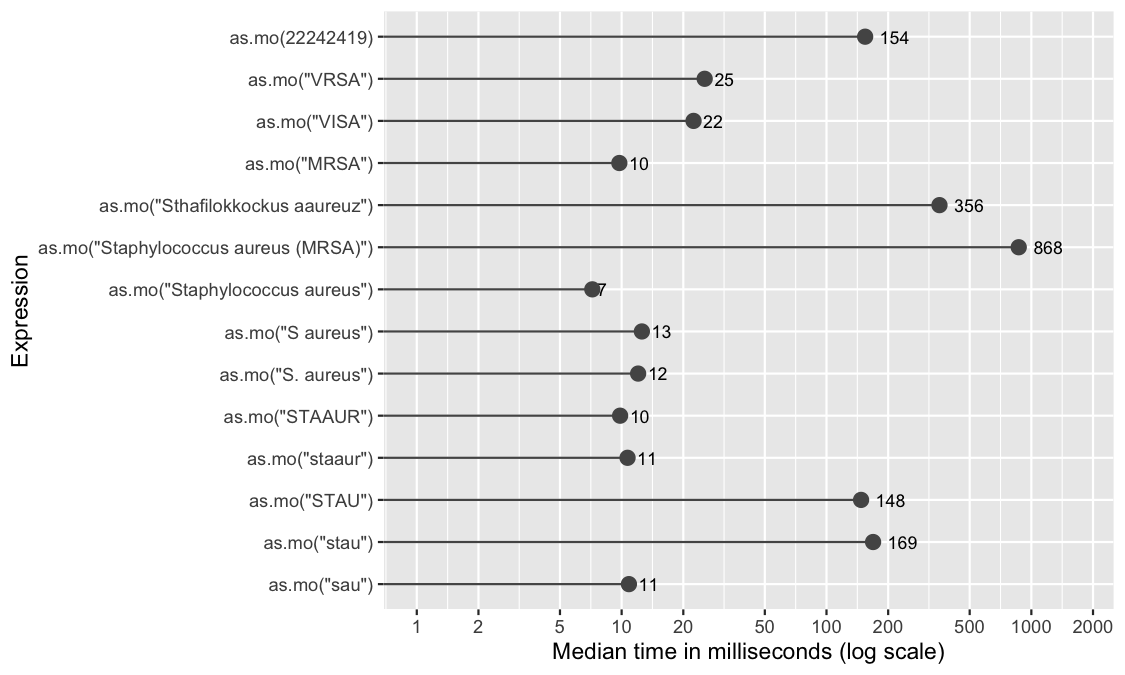
In the table above, all measurements are shown in milliseconds (thousands of seconds). A value of 5 milliseconds means it can determine 200 input values per second. It case of 100 milliseconds, this is only 10 input values per second.
To achieve this speed, the as.mo function also takes into account the prevalence of human pathogenic microorganisms. The downside of this is of course that less prevalent microorganisms will be determined less fast. See this example for the ID of Methanosarcina semesiae (B_MTHNSR_SEMS), a bug probably never found before in humans:
M.semesiae <- microbenchmark(as.mo("metsem"), as.mo("METSEM"), as.mo("M. semesiae"), as.mo("M. semesiae"), as.mo("Methanosarcina semesiae"), times = 10) print(M.semesiae, unit = "ms", signif = 4) # Unit: milliseconds # expr min lq mean median uq # as.mo("metsem") 146.500 150.900 173.300 183.300 191.800 # as.mo("METSEM") 145.700 153.400 169.300 172.300 185.300 # as.mo("M. semesiae") 8.586 8.790 9.909 10.140 10.250 # as.mo("M. semesiae") 8.613 8.719 12.350 9.756 10.210 # as.mo("Methanosarcina semesiae") 6.153 6.357 9.325 6.729 7.826 # max neval # 193.60 10 # 187.40 10 # 12.52 10 # 38.46 10 # 31.48 10
Looking up arbitrary codes of less prevalent microorganisms costs the most time. Full names (like Methanosarcina semesiae) are always very fast and only take some thousands of seconds to coerce - they are the most probable input from most data sets.
In the figure below, we compare Escherichia coli (which is very common) with Prevotella brevis (which is moderately common) and with Methanosarcina semesiae (which is uncommon):
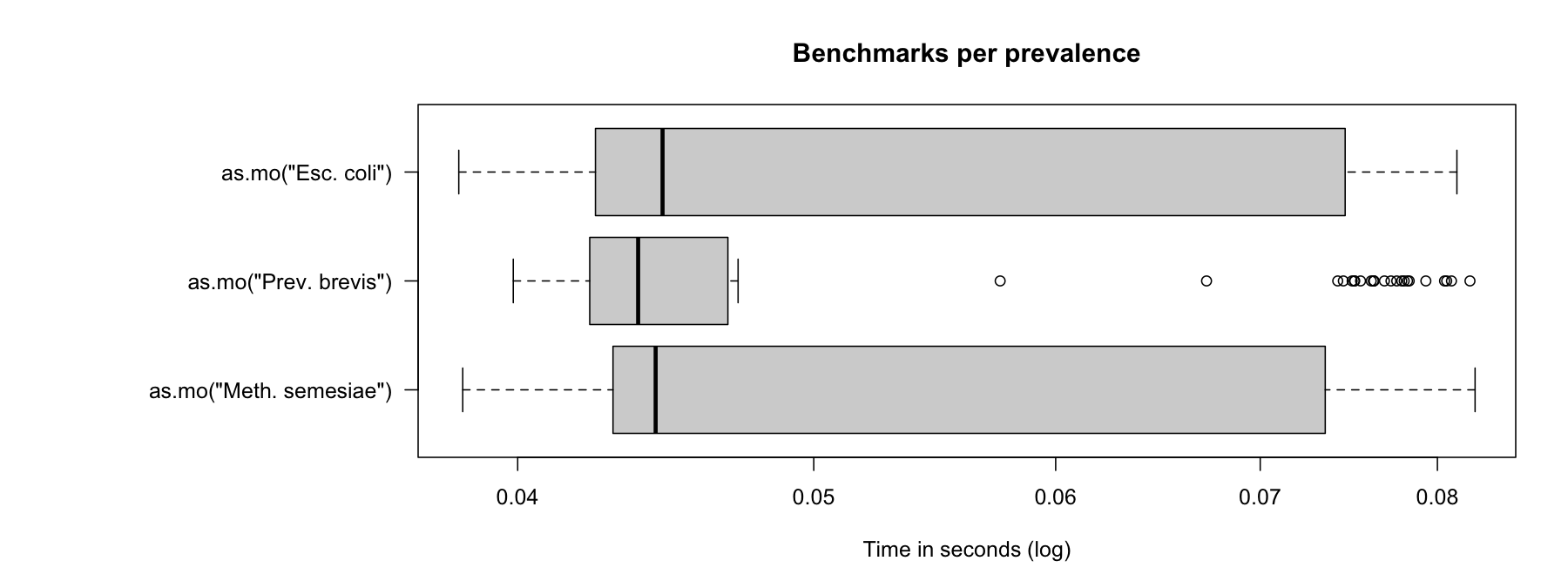
Uncommon microorganisms take some more time than common microorganisms. To further improve performance, two important calculations take almost no time at all: repetitive results and already precalculated results.
Repetitive results
Repetitive results are unique values that are present more than once. Unique values will only be calculated once by as.mo(). We will use mo_name() for this test - a helper function that returns the full microbial name (genus, species and possibly subspecies) which uses as.mo() internally.
library(dplyr)
# take all MO codes from the example_isolates data set x <- example_isolates$mo %>% # keep only the unique ones unique() %>% # pick 50 of them at random sample(50) %>% # paste that 10,000 times rep(10000) %>% # scramble it sample() # got indeed 50 times 10,000 = half a million? length(x) # [1] 500000 # and how many unique values do we have? n_distinct(x) # [1] 50 # now let's see: run_it <- microbenchmark(mo_name(x), times = 10) print(run_it, unit = "ms", signif = 3) # Unit: milliseconds # expr min lq mean median uq max neval # mo_name(x) 1660 1700 1760 1750 1810 1910 10
So transforming 500,000 values (!!) of 50 unique values only takes 1.75 seconds. You only lose time on your unique input values.
Precalculated results
What about precalculated results? If the input is an already precalculated result of a helper function like mo_name(), it almost doesn’t take any time at all (see ‘C’ below):
run_it <- microbenchmark(A = mo_name("B_STPHY_AURS"), B = mo_name("S. aureus"), C = mo_name("Staphylococcus aureus"), times = 10) print(run_it, unit = "ms", signif = 3) # Unit: milliseconds # expr min lq mean median uq max neval # A 5.650 6.030 6.36 6.430 6.660 7.130 10 # B 9.860 9.890 14.20 10.900 11.200 46.300 10 # C 0.232 0.237 0.30 0.302 0.355 0.369 10
So going from mo_name("Staphylococcus aureus") to "Staphylococcus aureus" takes 0.0003 seconds - it doesn’t even start calculating if the result would be the same as the expected resulting value. That goes for all helper functions:
run_it <- microbenchmark(A = mo_species("aureus"), B = mo_genus("Staphylococcus"), C = mo_name("Staphylococcus aureus"), D = mo_family("Staphylococcaceae"), E = mo_order("Bacillales"), F = mo_class("Bacilli"), G = mo_phylum("Firmicutes"), H = mo_kingdom("Bacteria"), times = 10) print(run_it, unit = "ms", signif = 3) # Unit: milliseconds # expr min lq mean median uq max neval # A 0.209 0.214 0.229 0.221 0.229 0.299 10 # B 0.199 0.206 0.225 0.209 0.214 0.373 10 # C 0.201 0.207 0.217 0.213 0.222 0.247 10 # D 0.200 0.203 0.214 0.206 0.222 0.266 10 # E 0.200 0.200 0.213 0.209 0.216 0.264 10 # F 0.195 0.205 0.216 0.207 0.217 0.284 10 # G 0.191 0.194 0.206 0.203 0.206 0.261 10 # H 0.190 0.195 0.205 0.198 0.209 0.256 10
Of course, when running mo_phylum("Firmicutes") the function has zero knowledge about the actual microorganism, namely S. aureus. But since the result would be "Firmicutes" anyway, there is no point in calculating the result. And because this package ‘knows’ all phyla of all known bacteria (according to the Catalogue of Life), it can just return the initial value immediately.
Results in other languages
When the system language is non-English and supported by this AMR package, some functions will have a translated result. This almost does’t take extra time:
mo_name("CoNS", language = "en") # or just mo_name("CoNS") on an English system # [1] "Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus (CoNS)" mo_name("CoNS", language = "es") # or just mo_name("CoNS") on a Spanish system # [1] "Staphylococcus coagulasa negativo (SCN)" mo_name("CoNS", language = "nl") # or just mo_name("CoNS") on a Dutch system # [1] "Coagulase-negatieve Staphylococcus (CNS)" run_it <- microbenchmark(en = mo_name("CoNS", language = "en"), de = mo_name("CoNS", language = "de"), nl = mo_name("CoNS", language = "nl"), es = mo_name("CoNS", language = "es"), it = mo_name("CoNS", language = "it"), fr = mo_name("CoNS", language = "fr"), pt = mo_name("CoNS", language = "pt"), times = 100) print(run_it, unit = "ms", signif = 4) # Unit: milliseconds # expr min lq mean median uq max neval # en 20.58 21.00 24.57 21.31 21.81 65.96 100 # de 21.28 21.81 25.34 22.15 22.73 62.52 100 # nl 25.15 25.68 32.14 26.03 27.25 167.40 100 # es 21.35 21.78 27.39 22.14 23.29 67.97 100 # it 21.42 21.83 26.19 22.31 22.84 71.71 100 # fr 21.43 21.82 27.43 22.25 23.39 69.29 100 # pt 21.42 21.92 28.71 22.23 22.89 187.40 100
Currently supported are German, Dutch, Spanish, Italian, French and Portuguese.